注意
点击 这里 下载完整的示例代码
使用 Wav2Vec2 进行语音识别¶
作者:Moto Hira
本教程展示了如何使用 wav2vec 2.0 的预训练模型 [论文] 进行语音识别。
概述¶
语音识别的过程如下所示。
从音频波形中提取声学特征
逐帧估计声学特征的类别
从类别概率序列生成假设
Torchaudio 提供了对预训练权重和相关信息(如期望的采样率和类别标签)的便捷访问。它们被捆绑在一起,可在 torchaudio.pipelines 模块下找到。
准备¶
import torch
import torchaudio
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
torch.random.manual_seed(0)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(device)
2.10.0.dev20251013+cu126
2.8.0a0+1d65bbe
cuda
import IPython
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torchaudio.utils import _download_asset
SPEECH_FILE = _download_asset("tutorial-assets/Lab41-SRI-VOiCES-src-sp0307-ch127535-sg0042.wav")
100.0%
创建管道¶
首先,我们将创建一个执行特征提取和分类的 Wav2Vec2 模型。
Torchaudio 中有两种类型的 Wav2Vec2 预训练权重可用。一种是为 ASR 任务进行了微调的,另一种是没有微调的。
Wav2Vec2 (和 HuBERT) 模型以自监督方式进行训练。它们首先仅使用音频进行表示学习,然后使用附加标签为特定任务进行微调。
未经微调的预训练权重也可以为其他下游任务进行微调,但本教程不涵盖此内容。
这里我们将使用 torchaudio.pipelines.WAV2VEC2_ASR_BASE_960H。
在 torchaudio.pipelines 中有多个预训练模型可用。请查看文档以了解它们是如何训练的详细信息。
bundle 对象提供了实例化模型和其他信息的接口。采样率和类别标签如下所示。
bundle = torchaudio.pipelines.WAV2VEC2_ASR_BASE_960H
print("Sample Rate:", bundle.sample_rate)
print("Labels:", bundle.get_labels())
Sample Rate: 16000
Labels: ('-', '|', 'E', 'T', 'A', 'O', 'N', 'I', 'H', 'S', 'R', 'D', 'L', 'U', 'M', 'W', 'C', 'F', 'G', 'Y', 'P', 'B', 'V', 'K', "'", 'X', 'J', 'Q', 'Z')
模型可以按如下方式构建。此过程将自动获取预训练权重并将其加载到模型中。
model = bundle.get_model().to(device)
print(model.__class__)
Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/torchaudio/models/wav2vec2_fairseq_base_ls960_asr_ls960.pth" to /root/.cache/torch/hub/checkpoints/wav2vec2_fairseq_base_ls960_asr_ls960.pth
0.0%
0.1%
0.1%
0.1%
0.2%
0.2%
0.2%
0.3%
0.3%
0.3%
0.4%
0.4%
0.5%
0.5%
0.5%
0.6%
0.6%
0.6%
0.7%
0.7%
0.7%
0.8%
0.8%
0.8%
0.9%
0.9%
0.9%
1.0%
1.0%
1.0%
1.1%
1.1%
1.1%
1.2%
1.2%
1.2%
1.3%
1.3%
1.4%
1.4%
1.4%
1.5%
1.5%
1.5%
1.6%
1.6%
1.6%
1.7%
1.7%
1.7%
1.8%
1.8%
1.8%
1.9%
1.9%
1.9%
2.0%
2.0%
2.0%
2.1%
2.1%
2.2%
2.2%
2.2%
2.3%
2.3%
2.3%
2.4%
2.4%
2.4%
2.5%
2.5%
2.5%
2.6%
2.6%
2.6%
2.7%
2.7%
2.7%
2.8%
2.8%
2.8%
2.9%
2.9%
3.0%
3.0%
3.0%
3.1%
3.1%
3.1%
3.2%
3.2%
3.2%
3.3%
3.3%
3.3%
3.4%
3.4%
3.4%
3.5%
3.5%
3.5%
3.6%
3.6%
3.6%
3.7%
3.7%
3.7%
3.8%
3.8%
3.9%
3.9%
3.9%
4.0%
4.0%
4.0%
4.1%
4.1%
4.1%
4.2%
4.2%
4.2%
4.3%
4.3%
4.3%
4.4%
4.4%
4.4%
4.5%
4.5%
4.5%
4.6%
4.6%
4.7%
4.7%
4.7%
4.8%
4.8%
4.8%
4.9%
4.9%
4.9%
5.0%
5.0%
5.0%
5.1%
5.1%
5.1%
5.2%
5.2%
5.2%
5.3%
5.3%
5.3%
5.4%
5.4%
5.4%
5.5%
5.5%
5.6%
5.6%
5.6%
5.7%
5.7%
5.7%
5.8%
5.8%
5.8%
5.9%
5.9%
5.9%
6.0%
6.0%
6.0%
6.1%
6.1%
6.1%
6.2%
6.2%
6.2%
6.3%
6.3%
6.4%
6.4%
6.4%
6.5%
6.5%
6.5%
6.6%
6.6%
6.6%
6.7%
6.7%
6.7%
6.8%
6.8%
6.8%
6.9%
6.9%
6.9%
7.0%
7.0%
7.0%
7.1%
7.1%
7.1%
7.2%
7.2%
7.3%
7.3%
7.3%
7.4%
7.4%
7.4%
7.5%
7.5%
7.5%
7.6%
7.6%
7.6%
7.7%
7.7%
7.7%
7.8%
7.8%
7.8%
7.9%
7.9%
7.9%
8.0%
8.0%
8.1%
8.1%
8.1%
8.2%
8.2%
8.2%
8.3%
8.3%
8.3%
8.4%
8.4%
8.4%
8.5%
8.5%
8.5%
8.6%
8.6%
8.6%
8.7%
8.7%
8.7%
8.8%
8.8%
8.9%
8.9%
8.9%
9.0%
9.0%
9.0%
9.1%
9.1%
9.1%
9.2%
9.2%
9.2%
9.3%
9.3%
9.3%
9.4%
9.4%
9.4%
9.5%
9.5%
9.5%
9.6%
9.6%
9.6%
9.7%
9.7%
9.8%
9.8%
9.8%
9.9%
9.9%
9.9%
10.0%
10.0%
10.0%
10.1%
10.1%
10.1%
10.2%
10.2%
10.2%
10.3%
10.3%
10.3%
10.4%
10.4%
10.4%
10.5%
10.5%
10.6%
10.6%
10.6%
10.7%
10.7%
10.7%
10.8%
10.8%
10.8%
10.9%
10.9%
10.9%
11.0%
11.0%
11.0%
11.1%
11.1%
11.1%
11.2%
11.2%
11.2%
11.3%
11.3%
11.3%
11.4%
11.4%
11.5%
11.5%
11.5%
11.6%
11.6%
11.6%
11.7%
11.7%
11.7%
11.8%
11.8%
11.8%
11.9%
11.9%
11.9%
12.0%
12.0%
12.0%
12.1%
12.1%
12.1%
12.2%
12.2%
12.3%
12.3%
12.3%
12.4%
12.4%
12.4%
12.5%
12.5%
12.5%
12.6%
12.6%
12.6%
12.7%
12.7%
12.7%
12.8%
12.8%
12.8%
12.9%
12.9%
12.9%
13.0%
13.0%
13.0%
13.1%
13.1%
13.2%
13.2%
13.2%
13.3%
13.3%
13.3%
13.4%
13.4%
13.4%
13.5%
13.5%
13.5%
13.6%
13.6%
13.6%
13.7%
13.7%
13.7%
13.8%
13.8%
13.8%
13.9%
13.9%
14.0%
14.0%
14.0%
14.1%
14.1%
14.1%
14.2%
14.2%
14.2%
14.3%
14.3%
14.3%
14.4%
14.4%
14.4%
14.5%
14.5%
14.5%
14.6%
14.6%
14.6%
14.7%
14.7%
14.8%
14.8%
14.8%
14.9%
14.9%
14.9%
15.0%
15.0%
15.0%
15.1%
15.1%
15.1%
15.2%
15.2%
15.2%
15.3%
15.3%
15.3%
15.4%
15.4%
15.4%
15.5%
15.5%
15.5%
15.6%
15.6%
15.7%
15.7%
15.7%
15.8%
15.8%
15.8%
15.9%
15.9%
15.9%
16.0%
16.0%
16.0%
16.1%
16.1%
16.1%
16.2%
16.2%
16.2%
16.3%
16.3%
16.3%
16.4%
16.4%
16.5%
16.5%
16.5%
16.6%
16.6%
16.6%
16.7%
16.7%
16.7%
16.8%
16.8%
16.8%
16.9%
16.9%
16.9%
17.0%
17.0%
17.0%
17.1%
17.1%
17.1%
17.2%
17.2%
17.2%
17.3%
17.3%
17.4%
17.4%
17.4%
17.5%
17.5%
17.5%
17.6%
17.6%
17.6%
17.7%
17.7%
17.7%
17.8%
17.8%
17.8%
17.9%
17.9%
17.9%
18.0%
18.0%
18.0%
18.1%
18.1%
18.2%
18.2%
18.2%
18.3%
18.3%
18.3%
18.4%
18.4%
18.4%
18.5%
18.5%
18.5%
18.6%
18.6%
18.6%
18.7%
18.7%
18.7%
18.8%
18.8%
18.8%
18.9%
18.9%
18.9%
19.0%
19.0%
19.1%
19.1%
19.1%
19.2%
19.2%
19.2%
19.3%
19.3%
19.3%
19.4%
19.4%
19.4%
19.5%
19.5%
19.5%
19.6%
19.6%
19.6%
19.7%
19.7%
19.7%
19.8%
19.8%
19.9%
19.9%
19.9%
20.0%
20.0%
20.0%
20.1%
20.1%
20.1%
20.2%
20.2%
20.2%
20.3%
20.3%
20.3%
20.4%
20.4%
20.4%
20.5%
20.5%
20.5%
20.6%
20.6%
20.7%
20.7%
20.7%
20.8%
20.8%
20.8%
20.9%
20.9%
20.9%
21.0%
21.0%
21.0%
21.1%
21.1%
21.1%
21.2%
21.2%
21.2%
21.3%
21.3%
21.3%
21.4%
21.4%
21.4%
21.5%
21.5%
21.6%
21.6%
21.6%
21.7%
21.7%
21.7%
21.8%
21.8%
21.8%
21.9%
21.9%
21.9%
22.0%
22.0%
22.0%
22.1%
22.1%
22.1%
22.2%
22.2%
22.2%
22.3%
22.3%
22.4%
22.4%
22.4%
22.5%
22.5%
22.5%
22.6%
22.6%
22.6%
22.7%
22.7%
22.7%
22.8%
22.8%
22.8%
22.9%
22.9%
22.9%
23.0%
23.0%
23.0%
23.1%
23.1%
23.1%
23.2%
23.2%
23.3%
23.3%
23.3%
23.4%
23.4%
23.4%
23.5%
23.5%
23.5%
23.6%
23.6%
23.6%
23.7%
23.7%
23.7%
23.8%
23.8%
23.8%
23.9%
23.9%
23.9%
24.0%
24.0%
24.1%
24.1%
24.1%
24.2%
24.2%
24.2%
24.3%
24.3%
24.3%
24.4%
24.4%
24.4%
24.5%
24.5%
24.5%
24.6%
24.6%
24.6%
24.7%
24.7%
24.7%
24.8%
24.8%
24.8%
24.9%
24.9%
25.0%
25.0%
25.0%
25.1%
25.1%
25.1%
25.2%
25.2%
25.2%
25.3%
25.3%
25.3%
25.4%
25.4%
25.4%
25.5%
25.5%
25.5%
25.6%
25.6%
25.6%
25.7%
25.7%
25.8%
25.8%
25.8%
25.9%
25.9%
25.9%
26.0%
26.0%
26.0%
26.1%
26.1%
26.1%
26.2%
26.2%
26.2%
26.3%
26.3%
26.3%
26.4%
26.4%
26.4%
26.5%
26.5%
26.6%
26.6%
26.6%
26.7%
26.7%
26.7%
26.8%
26.8%
26.8%
26.9%
26.9%
26.9%
27.0%
27.0%
27.0%
27.1%
27.1%
27.1%
27.2%
27.2%
27.2%
27.3%
27.3%
27.3%
27.4%
27.4%
27.5%
27.5%
27.5%
27.6%
27.6%
27.6%
27.7%
27.7%
27.7%
27.8%
27.8%
27.8%
27.9%
27.9%
27.9%
28.0%
28.0%
28.0%
28.1%
28.1%
28.1%
28.2%
28.2%
28.3%
28.3%
28.3%
28.4%
28.4%
28.4%
28.5%
28.5%
28.5%
28.6%
28.6%
28.6%
28.7%
28.7%
28.7%
28.8%
28.8%
28.8%
28.9%
28.9%
28.9%
29.0%
29.0%
29.0%
29.1%
29.1%
29.2%
29.2%
29.2%
29.3%
29.3%
29.3%
29.4%
29.4%
29.4%
29.5%
29.5%
29.5%
29.6%
29.6%
29.6%
29.7%
29.7%
29.7%
29.8%
29.8%
29.8%
29.9%
29.9%
30.0%
30.0%
30.0%
30.1%
30.1%
30.1%
30.2%
30.2%
30.2%
30.3%
30.3%
30.3%
30.4%
30.4%
30.4%
30.5%
30.5%
30.5%
30.6%
30.6%
30.6%
30.7%
30.7%
30.7%
30.8%
30.8%
30.9%
30.9%
30.9%
31.0%
31.0%
31.0%
31.1%
31.1%
31.1%
31.2%
31.2%
31.2%
31.3%
31.3%
31.3%
31.4%
31.4%
31.4%
31.5%
31.5%
31.5%
31.6%
31.6%
31.7%
31.7%
31.7%
31.8%
31.8%
31.8%
31.9%
31.9%
31.9%
32.0%
32.0%
32.0%
32.1%
32.1%
32.1%
32.2%
32.2%
32.2%
32.3%
32.3%
32.3%
32.4%
32.4%
32.5%
32.5%
32.5%
32.6%
32.6%
32.6%
32.7%
32.7%
32.7%
32.8%
32.8%
32.8%
32.9%
32.9%
32.9%
33.0%
33.0%
33.0%
33.1%
33.1%
33.1%
33.2%
33.2%
33.2%
33.3%
33.3%
33.4%
33.4%
33.4%
33.5%
33.5%
33.5%
33.6%
33.6%
33.6%
33.7%
33.7%
33.7%
33.8%
33.8%
33.8%
33.9%
33.9%
33.9%
34.0%
34.0%
34.0%
34.1%
34.1%
34.2%
34.2%
34.2%
34.3%
34.3%
34.3%
34.4%
34.4%
34.4%
34.5%
34.5%
34.5%
34.6%
34.6%
34.6%
34.7%
34.7%
34.7%
34.8%
34.8%
34.8%
34.9%
34.9%
34.9%
35.0%
35.0%
35.1%
35.1%
35.1%
35.2%
35.2%
35.2%
35.3%
35.3%
35.3%
35.4%
35.4%
35.4%
35.5%
35.5%
35.5%
35.6%
35.6%
35.6%
35.7%
35.7%
35.7%
35.8%
35.8%
35.9%
35.9%
35.9%
36.0%
36.0%
36.0%
36.1%
36.1%
36.1%
36.2%
36.2%
36.2%
36.3%
36.3%
36.3%
36.4%
36.4%
36.4%
36.5%
36.5%
36.5%
36.6%
36.6%
36.6%
36.7%
36.7%
36.8%
36.8%
36.8%
36.9%
36.9%
36.9%
37.0%
37.0%
37.0%
37.1%
37.1%
37.1%
37.2%
37.2%
37.2%
37.3%
37.3%
37.3%
37.4%
37.4%
37.4%
37.5%
37.5%
37.6%
37.6%
37.6%
37.7%
37.7%
37.7%
37.8%
37.8%
37.8%
37.9%
37.9%
37.9%
38.0%
38.0%
38.0%
38.1%
38.1%
38.1%
38.2%
38.2%
38.2%
38.3%
38.3%
38.4%
38.4%
38.4%
38.5%
38.5%
38.5%
38.6%
38.6%
38.6%
38.7%
38.7%
38.7%
38.8%
38.8%
38.8%
38.9%
38.9%
38.9%
39.0%
39.0%
39.0%
39.1%
39.1%
39.1%
39.2%
39.2%
39.3%
39.3%
39.3%
39.4%
39.4%
39.4%
39.5%
39.5%
39.5%
39.6%
39.6%
39.6%
39.7%
39.7%
39.7%
39.8%
39.8%
39.8%
39.9%
39.9%
39.9%
40.0%
40.0%
40.1%
40.1%
40.1%
40.2%
40.2%
40.2%
40.3%
40.3%
40.3%
40.4%
40.4%
40.4%
40.5%
40.5%
40.5%
40.6%
40.6%
40.6%
40.7%
40.7%
40.7%
40.8%
40.8%
40.8%
40.9%
40.9%
41.0%
41.0%
41.0%
41.1%
41.1%
41.1%
41.2%
41.2%
41.2%
41.3%
41.3%
41.3%
41.4%
41.4%
41.4%
41.5%
41.5%
41.5%
41.6%
41.6%
41.6%
41.7%
41.7%
41.8%
41.8%
41.8%
41.9%
41.9%
41.9%
42.0%
42.0%
42.0%
42.1%
42.1%
42.1%
42.2%
42.2%
42.2%
42.3%
42.3%
42.3%
42.4%
42.4%
42.4%
42.5%
42.5%
42.5%
42.6%
42.6%
42.7%
42.7%
42.7%
42.8%
42.8%
42.8%
42.9%
42.9%
42.9%
43.0%
43.0%
43.0%
43.1%
43.1%
43.1%
43.2%
43.2%
43.2%
43.3%
43.3%
43.3%
43.4%
43.4%
43.5%
43.5%
43.5%
43.6%
43.6%
43.6%
43.7%
43.7%
43.7%
43.8%
43.8%
43.8%
43.9%
43.9%
43.9%
44.0%
44.0%
44.0%
44.1%
44.1%
44.1%
44.2%
44.2%
44.3%
44.3%
44.3%
44.4%
44.4%
44.4%
44.5%
44.5%
44.5%
44.6%
44.6%
44.6%
44.7%
44.7%
44.7%
44.8%
44.8%
44.8%
44.9%
44.9%
44.9%
45.0%
45.0%
45.0%
45.1%
45.1%
45.2%
45.2%
45.2%
45.3%
45.3%
45.3%
45.4%
45.4%
45.4%
45.5%
45.5%
45.5%
45.6%
45.6%
45.6%
45.7%
45.7%
45.7%
45.8%
45.8%
45.8%
45.9%
45.9%
46.0%
46.0%
46.0%
46.1%
46.1%
46.1%
46.2%
46.2%
46.2%
46.3%
46.3%
46.3%
46.4%
46.4%
46.4%
46.5%
46.5%
46.5%
46.6%
46.6%
46.6%
46.7%
46.7%
46.7%
46.8%
46.8%
46.9%
46.9%
46.9%
47.0%
47.0%
47.0%
47.1%
47.1%
47.1%
47.2%
47.2%
47.2%
47.3%
47.3%
47.3%
47.4%
47.4%
47.4%
47.5%
47.5%
47.5%
47.6%
47.6%
47.7%
47.7%
47.7%
47.8%
47.8%
47.8%
47.9%
47.9%
47.9%
48.0%
48.0%
48.0%
48.1%
48.1%
48.1%
48.2%
48.2%
48.2%
48.3%
48.3%
48.3%
48.4%
48.4%
48.4%
48.5%
48.5%
48.6%
48.6%
48.6%
48.7%
48.7%
48.7%
48.8%
48.8%
48.8%
48.9%
48.9%
48.9%
49.0%
49.0%
49.0%
49.1%
49.1%
49.1%
49.2%
49.2%
49.2%
49.3%
49.3%
49.4%
49.4%
49.4%
49.5%
49.5%
49.5%
49.6%
49.6%
49.6%
49.7%
49.7%
49.7%
49.8%
49.8%
49.8%
49.9%
49.9%
49.9%
50.0%
50.0%
50.0%
50.1%
50.1%
50.2%
50.2%
50.2%
50.3%
50.3%
50.3%
50.4%
50.4%
50.4%
50.5%
50.5%
50.5%
50.6%
50.6%
50.6%
50.7%
50.7%
50.7%
50.8%
50.8%
50.8%
50.9%
50.9%
50.9%
51.0%
51.0%
51.1%
51.1%
51.1%
51.2%
51.2%
51.2%
51.3%
51.3%
51.3%
51.4%
51.4%
51.4%
51.5%
51.5%
51.5%
51.6%
51.6%
51.6%
51.7%
51.7%
51.7%
51.8%
51.8%
51.9%
51.9%
51.9%
52.0%
52.0%
52.0%
52.1%
52.1%
52.1%
52.2%
52.2%
52.2%
52.3%
52.3%
52.3%
52.4%
52.4%
52.4%
52.5%
52.5%
52.5%
52.6%
52.6%
52.6%
52.7%
52.7%
52.8%
52.8%
52.8%
52.9%
52.9%
52.9%
53.0%
53.0%
53.0%
53.1%
53.1%
53.1%
53.2%
53.2%
53.2%
53.3%
53.3%
53.3%
53.4%
53.4%
53.4%
53.5%
53.5%
53.6%
53.6%
53.6%
53.7%
53.7%
53.7%
53.8%
53.8%
53.8%
53.9%
53.9%
53.9%
54.0%
54.0%
54.0%
54.1%
54.1%
54.1%
54.2%
54.2%
54.2%
54.3%
54.3%
54.3%
54.4%
54.4%
54.5%
54.5%
54.5%
54.6%
54.6%
54.6%
54.7%
54.7%
54.7%
54.8%
54.8%
54.8%
54.9%
54.9%
54.9%
55.0%
55.0%
55.0%
55.1%
55.1%
55.1%
55.2%
55.2%
55.3%
55.3%
55.3%
55.4%
55.4%
55.4%
55.5%
55.5%
55.5%
55.6%
55.6%
55.6%
55.7%
55.7%
55.7%
55.8%
55.8%
55.8%
55.9%
55.9%
55.9%
56.0%
56.0%
56.1%
56.1%
56.1%
56.2%
56.2%
56.2%
56.3%
56.3%
56.3%
56.4%
56.4%
56.4%
56.5%
56.5%
56.5%
56.6%
56.6%
56.6%
56.7%
56.7%
56.7%
56.8%
56.8%
56.8%
56.9%
56.9%
57.0%
57.0%
57.0%
57.1%
57.1%
57.1%
57.2%
57.2%
57.2%
57.3%
57.3%
57.3%
57.4%
57.4%
57.4%
57.5%
57.5%
57.5%
57.6%
57.6%
57.6%
57.7%
57.7%
57.8%
57.8%
57.8%
57.9%
57.9%
57.9%
58.0%
58.0%
58.0%
58.1%
58.1%
58.1%
58.2%
58.2%
58.2%
58.3%
58.3%
58.3%
58.4%
58.4%
58.4%
58.5%
58.5%
58.5%
58.6%
58.6%
58.7%
58.7%
58.7%
58.8%
58.8%
58.8%
58.9%
58.9%
58.9%
59.0%
59.0%
59.0%
59.1%
59.1%
59.1%
59.2%
59.2%
59.2%
59.3%
59.3%
59.3%
59.4%
59.4%
59.5%
59.5%
59.5%
59.6%
59.6%
59.6%
59.7%
59.7%
59.7%
59.8%
59.8%
59.8%
59.9%
59.9%
59.9%
60.0%
60.0%
60.0%
60.1%
60.1%
60.1%
60.2%
60.2%
60.2%
60.3%
60.3%
60.4%
60.4%
60.4%
60.5%
60.5%
60.5%
60.6%
60.6%
60.6%
60.7%
60.7%
60.7%
60.8%
60.8%
60.8%
60.9%
60.9%
60.9%
61.0%
61.0%
61.0%
61.1%
61.1%
61.2%
61.2%
61.2%
61.3%
61.3%
61.3%
61.4%
61.4%
61.4%
61.5%
61.5%
61.5%
61.6%
61.6%
61.6%
61.7%
61.7%
61.7%
61.8%
61.8%
61.8%
61.9%
61.9%
62.0%
62.0%
62.0%
62.1%
62.1%
62.1%
62.2%
62.2%
62.2%
62.3%
62.3%
62.3%
62.4%
62.4%
62.4%
62.5%
62.5%
62.5%
62.6%
62.6%
62.6%
62.7%
62.7%
62.7%
62.8%
62.8%
62.9%
62.9%
62.9%
63.0%
63.0%
63.0%
63.1%
63.1%
63.1%
63.2%
63.2%
63.2%
63.3%
63.3%
63.3%
63.4%
63.4%
63.4%
63.5%
63.5%
63.5%
63.6%
63.6%
63.7%
63.7%
63.7%
63.8%
63.8%
63.8%
63.9%
63.9%
63.9%
64.0%
64.0%
64.0%
64.1%
64.1%
64.1%
64.2%
64.2%
64.2%
64.3%
64.3%
64.3%
64.4%
64.4%
64.4%
64.5%
64.5%
64.6%
64.6%
64.6%
64.7%
64.7%
64.7%
64.8%
64.8%
64.8%
64.9%
64.9%
64.9%
65.0%
65.0%
65.0%
65.1%
65.1%
65.1%
65.2%
65.2%
65.2%
65.3%
65.3%
65.4%
65.4%
65.4%
65.5%
65.5%
65.5%
65.6%
65.6%
65.6%
65.7%
65.7%
65.7%
65.8%
65.8%
65.8%
65.9%
65.9%
65.9%
66.0%
66.0%
66.0%
66.1%
66.1%
66.1%
66.2%
66.2%
66.3%
66.3%
66.3%
66.4%
66.4%
66.4%
66.5%
66.5%
66.5%
66.6%
66.6%
66.6%
66.7%
66.7%
66.7%
66.8%
66.8%
66.8%
66.9%
66.9%
66.9%
67.0%
67.0%
67.1%
67.1%
67.1%
67.2%
67.2%
67.2%
67.3%
67.3%
67.3%
67.4%
67.4%
67.4%
67.5%
67.5%
67.5%
67.6%
67.6%
67.6%
67.7%
67.7%
67.7%
67.8%
67.8%
67.9%
67.9%
67.9%
68.0%
68.0%
68.0%
68.1%
68.1%
68.1%
68.2%
68.2%
68.2%
68.3%
68.3%
68.3%
68.4%
68.4%
68.4%
68.5%
68.5%
68.5%
68.6%
68.6%
68.6%
68.7%
68.7%
68.8%
68.8%
68.8%
68.9%
68.9%
68.9%
69.0%
69.0%
69.0%
69.1%
69.1%
69.1%
69.2%
69.2%
69.2%
69.3%
69.3%
69.3%
69.4%
69.4%
69.4%
69.5%
69.5%
69.6%
69.6%
69.6%
69.7%
69.7%
69.7%
69.8%
69.8%
69.8%
69.9%
69.9%
69.9%
70.0%
70.0%
70.0%
70.1%
70.1%
70.1%
70.2%
70.2%
70.2%
70.3%
70.3%
70.3%
70.4%
70.4%
70.5%
70.5%
70.5%
70.6%
70.6%
70.6%
70.7%
70.7%
70.7%
70.8%
70.8%
70.8%
70.9%
70.9%
70.9%
71.0%
71.0%
71.0%
71.1%
71.1%
71.1%
71.2%
71.2%
71.3%
71.3%
71.3%
71.4%
71.4%
71.4%
71.5%
71.5%
71.5%
71.6%
71.6%
71.6%
71.7%
71.7%
71.7%
71.8%
71.8%
71.8%
71.9%
71.9%
71.9%
72.0%
72.0%
72.0%
72.1%
72.1%
72.2%
72.2%
72.2%
72.3%
72.3%
72.3%
72.4%
72.4%
72.4%
72.5%
72.5%
72.5%
72.6%
72.6%
72.6%
72.7%
72.7%
72.7%
72.8%
72.8%
72.8%
72.9%
72.9%
73.0%
73.0%
73.0%
73.1%
73.1%
73.1%
73.2%
73.2%
73.2%
73.3%
73.3%
73.3%
73.4%
73.4%
73.4%
73.5%
73.5%
73.5%
73.6%
73.6%
73.6%
73.7%
73.7%
73.8%
73.8%
73.8%
73.9%
73.9%
73.9%
74.0%
74.0%
74.0%
74.1%
74.1%
74.1%
74.2%
74.2%
74.2%
74.3%
74.3%
74.3%
74.4%
74.4%
74.4%
74.5%
74.5%
74.5%
74.6%
74.6%
74.7%
74.7%
74.7%
74.8%
74.8%
74.8%
74.9%
74.9%
74.9%
75.0%
75.0%
75.0%
75.1%
75.1%
75.1%
75.2%
75.2%
75.2%
75.3%
75.3%
75.3%
75.4%
75.4%
75.5%
75.5%
75.5%
75.6%
75.6%
75.6%
75.7%
75.7%
75.7%
75.8%
75.8%
75.8%
75.9%
75.9%
75.9%
76.0%
76.0%
76.0%
76.1%
76.1%
76.1%
76.2%
76.2%
76.2%
76.3%
76.3%
76.4%
76.4%
76.4%
76.5%
76.5%
76.5%
76.6%
76.6%
76.6%
76.7%
76.7%
76.7%
76.8%
76.8%
76.8%
76.9%
76.9%
76.9%
77.0%
77.0%
77.0%
77.1%
77.1%
77.2%
77.2%
77.2%
77.3%
77.3%
77.3%
77.4%
77.4%
77.4%
77.5%
77.5%
77.5%
77.6%
77.6%
77.6%
77.7%
77.7%
77.7%
77.8%
77.8%
77.8%
77.9%
77.9%
77.9%
78.0%
78.0%
78.1%
78.1%
78.1%
78.2%
78.2%
78.2%
78.3%
78.3%
78.3%
78.4%
78.4%
78.4%
78.5%
78.5%
78.5%
78.6%
78.6%
78.6%
78.7%
78.7%
78.7%
78.8%
78.8%
78.9%
78.9%
78.9%
79.0%
79.0%
79.0%
79.1%
79.1%
79.1%
79.2%
79.2%
79.2%
79.3%
79.3%
79.3%
79.4%
79.4%
79.4%
79.5%
79.5%
79.5%
79.6%
79.6%
79.7%
79.7%
79.7%
79.8%
79.8%
79.8%
79.9%
79.9%
79.9%
80.0%
80.0%
80.0%
80.1%
80.1%
80.1%
80.2%
80.2%
80.2%
80.3%
80.3%
80.3%
80.4%
80.4%
80.4%
80.5%
80.5%
80.6%
80.6%
80.6%
80.7%
80.7%
80.7%
80.8%
80.8%
80.8%
80.9%
80.9%
80.9%
81.0%
81.0%
81.0%
81.1%
81.1%
81.1%
81.2%
81.2%
81.2%
81.3%
81.3%
81.4%
81.4%
81.4%
81.5%
81.5%
81.5%
81.6%
81.6%
81.6%
81.7%
81.7%
81.7%
81.8%
81.8%
81.8%
81.9%
81.9%
81.9%
82.0%
82.0%
82.0%
82.1%
82.1%
82.1%
82.2%
82.2%
82.3%
82.3%
82.3%
82.4%
82.4%
82.4%
82.5%
82.5%
82.5%
82.6%
82.6%
82.6%
82.7%
82.7%
82.7%
82.8%
82.8%
82.8%
82.9%
82.9%
82.9%
83.0%
83.0%
83.1%
83.1%
83.1%
83.2%
83.2%
83.2%
83.3%
83.3%
83.3%
83.4%
83.4%
83.4%
83.5%
83.5%
83.5%
83.6%
83.6%
83.6%
83.7%
83.7%
83.7%
83.8%
83.8%
83.8%
83.9%
83.9%
84.0%
84.0%
84.0%
84.1%
84.1%
84.1%
84.2%
84.2%
84.2%
84.3%
84.3%
84.3%
84.4%
84.4%
84.4%
84.5%
84.5%
84.5%
84.6%
84.6%
84.6%
84.7%
84.7%
84.8%
84.8%
84.8%
84.9%
84.9%
84.9%
85.0%
85.0%
85.0%
85.1%
85.1%
85.1%
85.2%
85.2%
85.2%
85.3%
85.3%
85.3%
85.4%
85.4%
85.4%
85.5%
85.5%
85.6%
85.6%
85.6%
85.7%
85.7%
85.7%
85.8%
85.8%
85.8%
85.9%
85.9%
85.9%
86.0%
86.0%
86.0%
86.1%
86.1%
86.1%
86.2%
86.2%
86.2%
86.3%
86.3%
86.3%
86.4%
86.4%
86.5%
86.5%
86.5%
86.6%
86.6%
86.6%
86.7%
86.7%
86.7%
86.8%
86.8%
86.8%
86.9%
86.9%
86.9%
87.0%
87.0%
87.0%
87.1%
87.1%
87.1%
87.2%
87.2%
87.3%
87.3%
87.3%
87.4%
87.4%
87.4%
87.5%
87.5%
87.5%
87.6%
87.6%
87.6%
87.7%
87.7%
87.7%
87.8%
87.8%
87.8%
87.9%
87.9%
87.9%
88.0%
88.0%
88.0%
88.1%
88.1%
88.2%
88.2%
88.2%
88.3%
88.3%
88.3%
88.4%
88.4%
88.4%
88.5%
88.5%
88.5%
88.6%
88.6%
88.6%
88.7%
88.7%
88.7%
88.8%
88.8%
88.8%
88.9%
88.9%
89.0%
89.0%
89.0%
89.1%
89.1%
89.1%
89.2%
89.2%
89.2%
89.3%
89.3%
89.3%
89.4%
89.4%
89.4%
89.5%
89.5%
89.5%
89.6%
89.6%
89.6%
89.7%
89.7%
89.7%
89.8%
89.8%
89.9%
89.9%
89.9%
90.0%
90.0%
90.0%
90.1%
90.1%
90.1%
90.2%
90.2%
90.2%
90.3%
90.3%
90.3%
90.4%
90.4%
90.4%
90.5%
90.5%
90.5%
90.6%
90.6%
90.7%
90.7%
90.7%
90.8%
90.8%
90.8%
90.9%
90.9%
90.9%
91.0%
91.0%
91.0%
91.1%
91.1%
91.1%
91.2%
91.2%
91.2%
91.3%
91.3%
91.3%
91.4%
91.4%
91.5%
91.5%
91.5%
91.6%
91.6%
91.6%
91.7%
91.7%
91.7%
91.8%
91.8%
91.8%
91.9%
91.9%
91.9%
92.0%
92.0%
92.0%
92.1%
92.1%
92.1%
92.2%
92.2%
92.2%
92.3%
92.3%
92.4%
92.4%
92.4%
92.5%
92.5%
92.5%
92.6%
92.6%
92.6%
92.7%
92.7%
92.7%
92.8%
92.8%
92.8%
92.9%
92.9%
92.9%
93.0%
93.0%
93.0%
93.1%
93.1%
93.2%
93.2%
93.2%
93.3%
93.3%
93.3%
93.4%
93.4%
93.4%
93.5%
93.5%
93.5%
93.6%
93.6%
93.6%
93.7%
93.7%
93.7%
93.8%
93.8%
93.8%
93.9%
93.9%
93.9%
94.0%
94.0%
94.1%
94.1%
94.1%
94.2%
94.2%
94.2%
94.3%
94.3%
94.3%
94.4%
94.4%
94.4%
94.5%
94.5%
94.5%
94.6%
94.6%
94.6%
94.7%
94.7%
94.7%
94.8%
94.8%
94.9%
94.9%
94.9%
95.0%
95.0%
95.0%
95.1%
95.1%
95.1%
95.2%
95.2%
95.2%
95.3%
95.3%
95.3%
95.4%
95.4%
95.4%
95.5%
95.5%
95.5%
95.6%
95.6%
95.6%
95.7%
95.7%
95.8%
95.8%
95.8%
95.9%
95.9%
95.9%
96.0%
96.0%
96.0%
96.1%
96.1%
96.1%
96.2%
96.2%
96.2%
96.3%
96.3%
96.3%
96.4%
96.4%
96.4%
96.5%
96.5%
96.6%
96.6%
96.6%
96.7%
96.7%
96.7%
96.8%
96.8%
96.8%
96.9%
96.9%
96.9%
97.0%
97.0%
97.0%
97.1%
97.1%
97.1%
97.2%
97.2%
97.2%
97.3%
97.3%
97.4%
97.4%
97.4%
97.5%
97.5%
97.5%
97.6%
97.6%
97.6%
97.7%
97.7%
97.7%
97.8%
97.8%
97.8%
97.9%
97.9%
97.9%
98.0%
98.0%
98.0%
98.1%
98.1%
98.1%
98.2%
98.2%
98.3%
98.3%
98.3%
98.4%
98.4%
98.4%
98.5%
98.5%
98.5%
98.6%
98.6%
98.6%
98.7%
98.7%
98.7%
98.8%
98.8%
98.8%
98.9%
98.9%
98.9%
99.0%
99.0%
99.1%
99.1%
99.1%
99.2%
99.2%
99.2%
99.3%
99.3%
99.3%
99.4%
99.4%
99.4%
99.5%
99.5%
99.5%
99.6%
99.6%
99.6%
99.7%
99.7%
99.7%
99.8%
99.8%
99.8%
99.9%
99.9%
100.0%
100.0%
100.0%
<class 'torchaudio.models.wav2vec2.model.Wav2Vec2Model'>
加载数据¶
我们将使用来自 VOiCES 数据集 的语音数据,该数据集是在 Creative Commos BY 4.0 许可下发布的。
IPython.display.Audio(SPEECH_FILE)
要加载数据,我们使用 torchaudio.load()。
如果采样率与管道期望的不同,我们可以使用 torchaudio.functional.resample() 进行重采样。
注意
torchaudio.functional.resample()也适用于 CUDA 张量。当对同一组采样率执行多次重采样时,使用
torchaudio.transforms.Resample可能会提高性能。
waveform, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(SPEECH_FILE)
waveform = waveform.to(device)
if sample_rate != bundle.sample_rate:
waveform = torchaudio.functional.resample(waveform, sample_rate, bundle.sample_rate)
提取声学特征¶
下一步是从音频中提取声学特征。
注意
为 ASR 任务微调的 Wav2Vec2 模型可以一步完成特征提取和分类,但为了本教程的方便,我们也在此展示如何执行特征提取。
with torch.inference_mode():
features, _ = model.extract_features(waveform)
返回的特征是张量列表。每个张量都是 Transformer 层的输出。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(len(features), 1, figsize=(16, 4.3 * len(features)))
for i, feats in enumerate(features):
ax[i].imshow(feats[0].cpu(), interpolation="nearest")
ax[i].set_title(f"Feature from transformer layer {i+1}")
ax[i].set_xlabel("Feature dimension")
ax[i].set_ylabel("Frame (time-axis)")
fig.tight_layout()
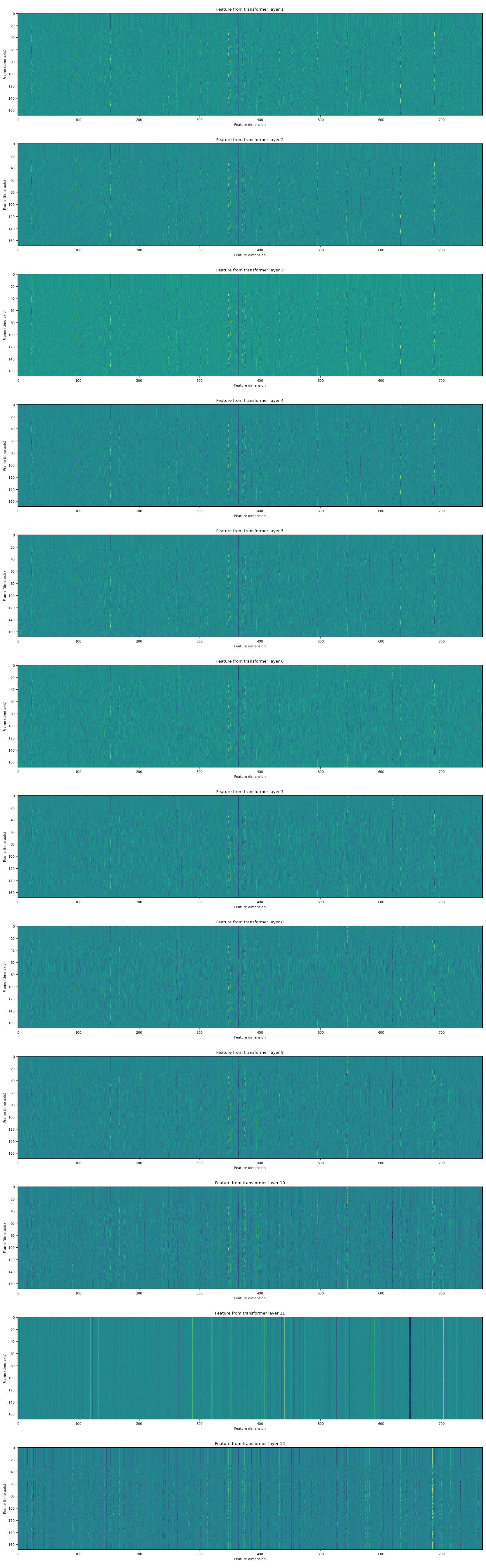
特征分类¶
提取声学特征后,下一步是将它们分类到一组类别中。
Wav2Vec2 模型提供了一个方法来一步完成特征提取和分类。
with torch.inference_mode():
emission, _ = model(waveform)
输出是以 logits 的形式。不是以概率的形式。
让我们可视化一下。
plt.imshow(emission[0].cpu().T, interpolation="nearest")
plt.title("Classification result")
plt.xlabel("Frame (time-axis)")
plt.ylabel("Class")
plt.tight_layout()
print("Class labels:", bundle.get_labels())
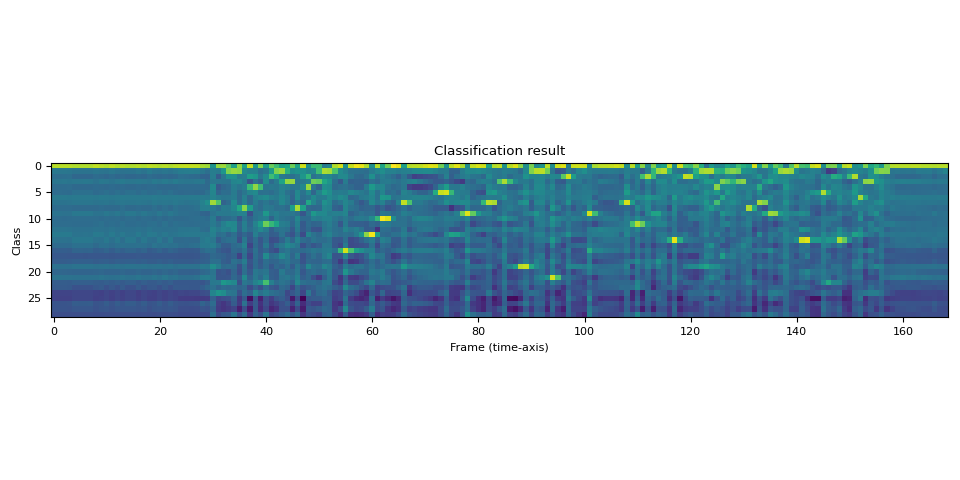
Class labels: ('-', '|', 'E', 'T', 'A', 'O', 'N', 'I', 'H', 'S', 'R', 'D', 'L', 'U', 'M', 'W', 'C', 'F', 'G', 'Y', 'P', 'B', 'V', 'K', "'", 'X', 'J', 'Q', 'Z')
我们可以看到,在时间线上存在一些明确的标签指示。
生成字幕¶
从标签概率序列中,我们现在想生成字幕。生成假设的过程通常称为“解码”。
解码比简单分类更复杂,因为某个时间步的解码会受到周围观测值的影响。
例如,考虑像 night 和 knight 这样的词。即使它们的先验概率分布不同(在典型的对话中,night 比 knight 出现得更频繁),为了准确地生成字幕,例如 a knight with a sword,解码过程必须推迟最终决定,直到它看到足够多的上下文。
已经提出了许多解码技术,它们需要外部资源,例如单词字典和语言模型。
在本教程中,为了简单起见,我们将执行贪婪解码,它不依赖于这些外部组件,而只是在每个时间步选择最佳假设。因此,不使用上下文信息,只能生成一个字幕。
我们首先定义贪婪解码算法。
class GreedyCTCDecoder(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, labels, blank=0):
super().__init__()
self.labels = labels
self.blank = blank
def forward(self, emission: torch.Tensor) -> str:
"""Given a sequence emission over labels, get the best path string
Args:
emission (Tensor): Logit tensors. Shape `[num_seq, num_label]`.
Returns:
str: The resulting transcript
"""
indices = torch.argmax(emission, dim=-1) # [num_seq,]
indices = torch.unique_consecutive(indices, dim=-1)
indices = [i for i in indices if i != self.blank]
return "".join([self.labels[i] for i in indices])
现在创建解码器对象并解码字幕。
decoder = GreedyCTCDecoder(labels=bundle.get_labels())
transcript = decoder(emission[0])
让我们检查结果并再次收听音频。
print(transcript)
IPython.display.Audio(SPEECH_FILE)
I|HAD|THAT|CURIOSITY|BESIDE|ME|AT|THIS|MOMENT|
ASR 模型使用一种称为连接时序分类 (CTC) 的损失函数进行了微调。CTC 损失的详细信息 在此 处进行了解释。在 CTC 中,空白标记 (ϵ) 是一个特殊标记,表示前一个符号的重复。在解码过程中,这些标记会被简单地忽略。
结论¶
在本教程中,我们研究了如何使用 Wav2Vec2ASRBundle 来执行声学特征提取和语音识别。构建模型和获取发射信号只需要两行代码。
model = torchaudio.pipelines.WAV2VEC2_ASR_BASE_960H.get_model()
emission = model(waveforms, ...)
脚本总运行时间: ( 0 分 5.806 秒)



