注意
点击此处下载完整示例代码
滤波器设计教程¶
作者:Moto Hira
警告
从 2.8 版本开始,我们正在重构 TorchAudio,以使其进入维护阶段。因此:
本教程中描述的 API 在 2.8 版本中已被弃用,并将在 2.9 版本中移除。
PyTorch 用于音频和视频的解码和编码功能正在被整合到 TorchCodec 中。
请参阅 https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 获取更多信息。
本教程展示如何创建基本的数字滤波器(脉冲响应)及其属性。
我们将研究基于窗函数 sinc 核和频率采样方法的低通、高通和带通滤波器。
import torch
import torchaudio
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2.8.0+cu126
2.8.0
from torchaudio.prototype.functional import frequency_impulse_response, sinc_impulse_response
窗函数 sinc 滤波器¶
Sinc 滤波器是一种理想化的滤波器,它在不影响较低频率的情况下去除截止频率以上的频率。
Sinc 滤波器在解析解中具有无限的滤波器宽度。在数值计算中,sinc 滤波器无法精确表达,因此需要进行近似。
窗函数 sinc 有限脉冲响应是 sinc 滤波器的一种近似。它是通过首先评估给定截止频率的 sinc 函数,然后截断滤波器裙边,并应用一个窗函数(例如 Hamming 窗)来减少截断引入的伪影而获得的。
sinc_impulse_response()生成给定截止频率的窗函数 sinc 脉冲响应。
低通滤波器¶
脉冲响应¶
创建 sinc IR 就像将截止频率值传递给sinc_impulse_response()一样简单。
cutoff = torch.linspace(0.0, 1.0, 9)
irs = sinc_impulse_response(cutoff, window_size=513)
print("Cutoff shape:", cutoff.shape)
print("Impulse response shape:", irs.shape)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/filter_design_tutorial.py:86: UserWarning: torchaudio.prototype.functional._dsp.sinc_impulse_response has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
irs = sinc_impulse_response(cutoff, window_size=513)
Cutoff shape: torch.Size([9])
Impulse response shape: torch.Size([9, 513])
让我们可视化生成的脉冲响应。
def plot_sinc_ir(irs, cutoff):
num_filts, window_size = irs.shape
half = window_size // 2
fig, axes = plt.subplots(num_filts, 1, sharex=True, figsize=(9.6, 8))
t = torch.linspace(-half, half - 1, window_size)
for ax, ir, coff, color in zip(axes, irs, cutoff, plt.cm.tab10.colors):
ax.plot(t, ir, linewidth=1.2, color=color, zorder=4, label=f"Cutoff: {coff}")
ax.legend(loc=(1.05, 0.2), handletextpad=0, handlelength=0)
ax.grid(True)
fig.suptitle(
"Impulse response of sinc low-pass filter for different cut-off frequencies\n"
"(Frequencies are relative to Nyquist frequency)"
)
axes[-1].set_xticks([i * half // 4 for i in range(-4, 5)])
fig.tight_layout()
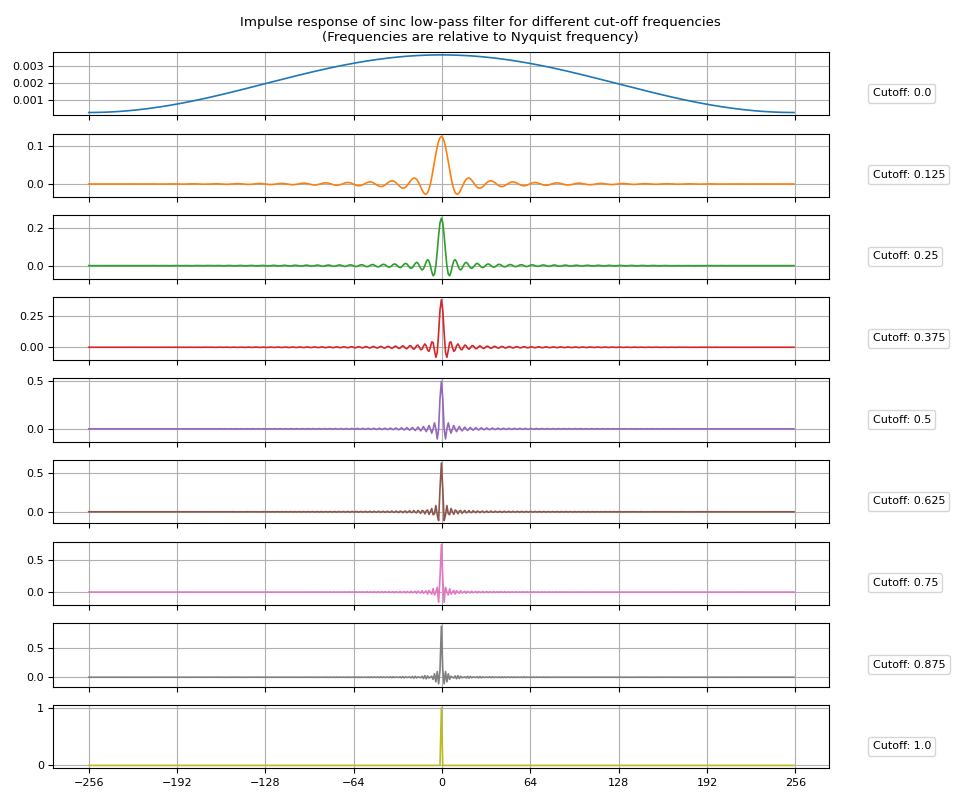
频率响应¶
接下来,让我们看看频率响应。简单地对脉冲响应应用傅里叶变换将得到频率响应。
frs = torch.fft.rfft(irs, n=2048, dim=1).abs()
让我们可视化生成的频率响应。
def plot_sinc_fr(frs, cutoff, band=False):
num_filts, num_fft = frs.shape
num_ticks = num_filts + 1 if band else num_filts
fig, axes = plt.subplots(num_filts, 1, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(9.6, 8))
for ax, fr, coff, color in zip(axes, frs, cutoff, plt.cm.tab10.colors):
ax.grid(True)
ax.semilogy(fr, color=color, zorder=4, label=f"Cutoff: {coff}")
ax.legend(loc=(1.05, 0.2), handletextpad=0, handlelength=0).set_zorder(3)
axes[-1].set(
ylim=[None, 100],
yticks=[1e-9, 1e-6, 1e-3, 1],
xticks=torch.linspace(0, num_fft, num_ticks),
xticklabels=[f"{i/(num_ticks - 1)}" for i in range(num_ticks)],
xlabel="Frequency",
)
fig.suptitle(
"Frequency response of sinc low-pass filter for different cut-off frequencies\n"
"(Frequencies are relative to Nyquist frequency)"
)
fig.tight_layout()
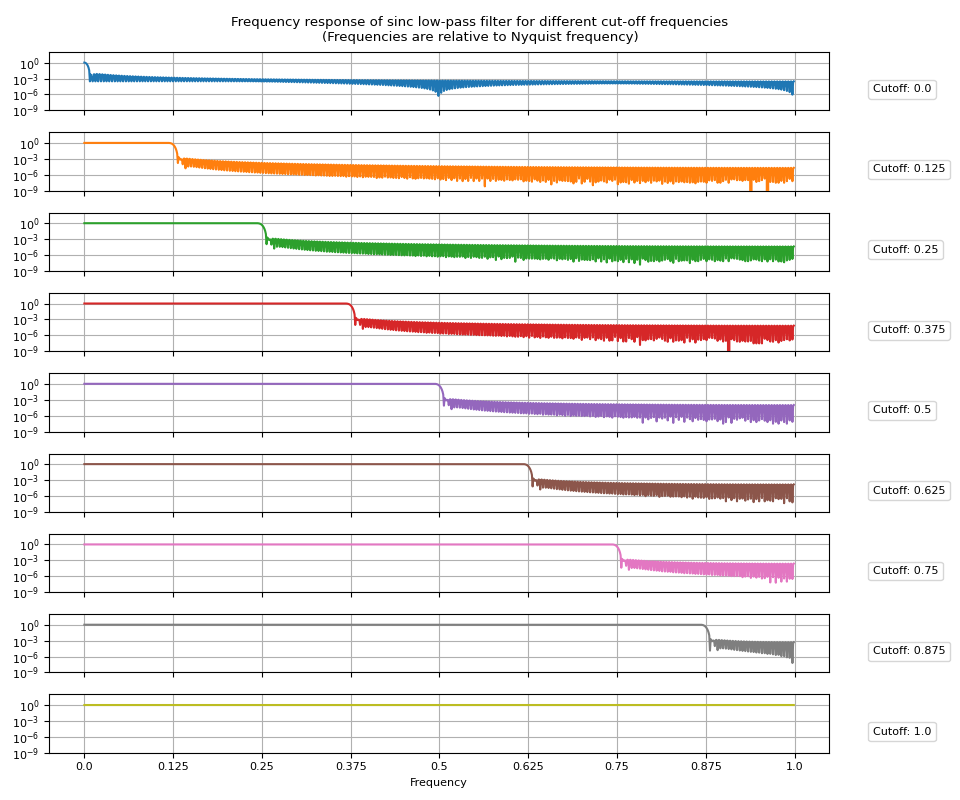
高通滤波器¶
高通滤波器可以通过从狄拉克δ函数中减去低通脉冲响应来获得。
将high_pass=True传递给sinc_impulse_response()将把返回的滤波器核更改为高通滤波器。
irs = sinc_impulse_response(cutoff, window_size=513, high_pass=True)
frs = torch.fft.rfft(irs, n=2048, dim=1).abs()
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/filter_design_tutorial.py:179: UserWarning: torchaudio.prototype.functional._dsp.sinc_impulse_response has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
irs = sinc_impulse_response(cutoff, window_size=513, high_pass=True)
脉冲响应¶
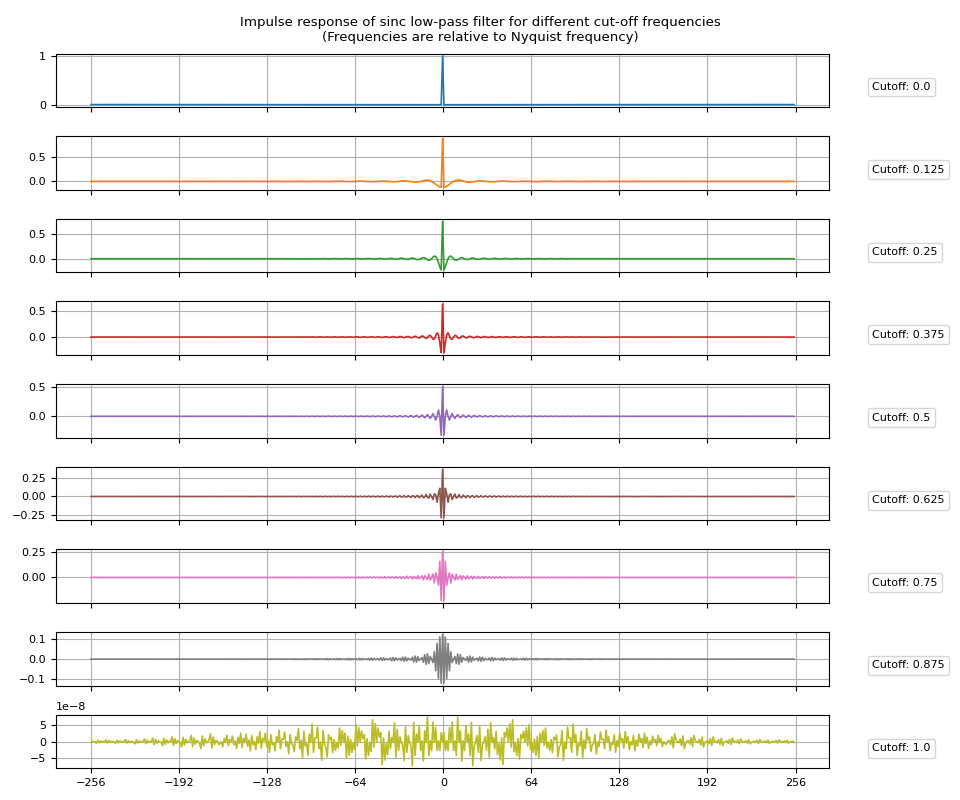
频率响应¶
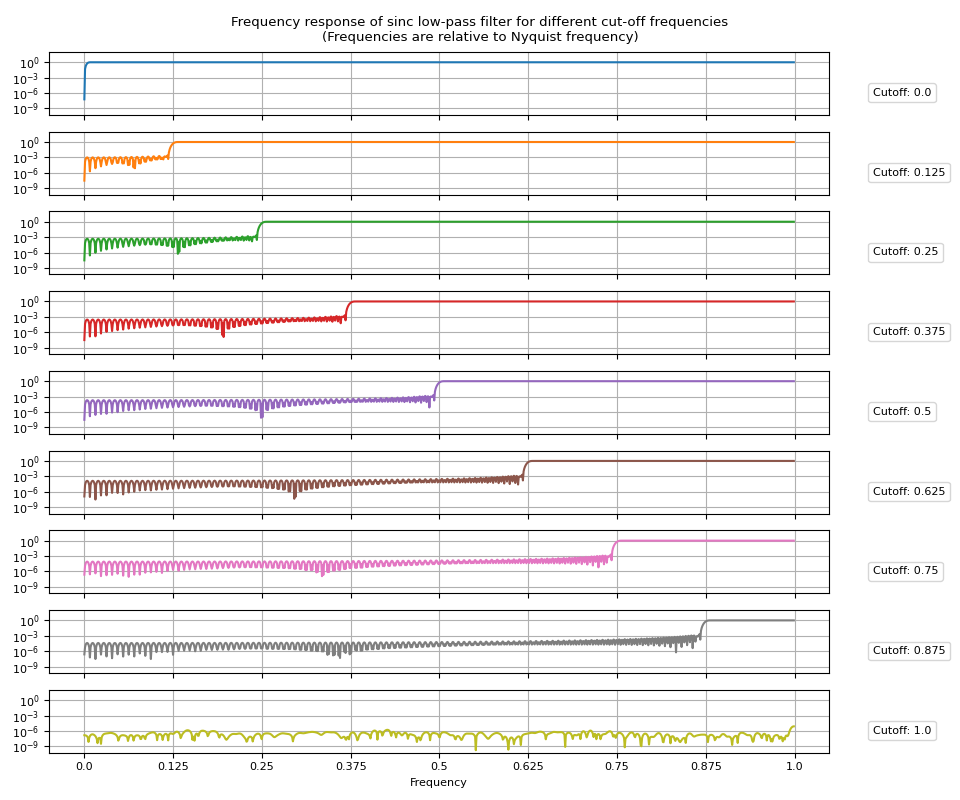
带通滤波器¶
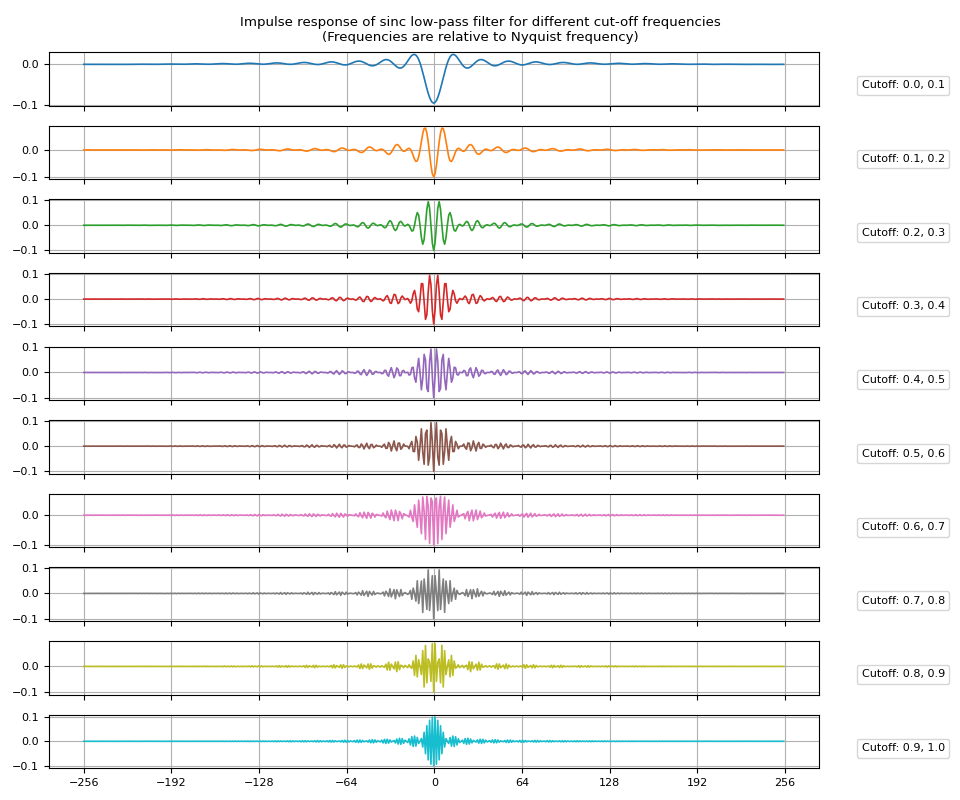
带通滤波器可以通过从上限低通滤波器中减去下限低通滤波器来获得。
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/filter_design_tutorial.py:210: UserWarning: torchaudio.prototype.functional._dsp.sinc_impulse_response has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
irs = sinc_impulse_response(c_low, window_size=513) - sinc_impulse_response(c_high, window_size=513)
脉冲响应¶
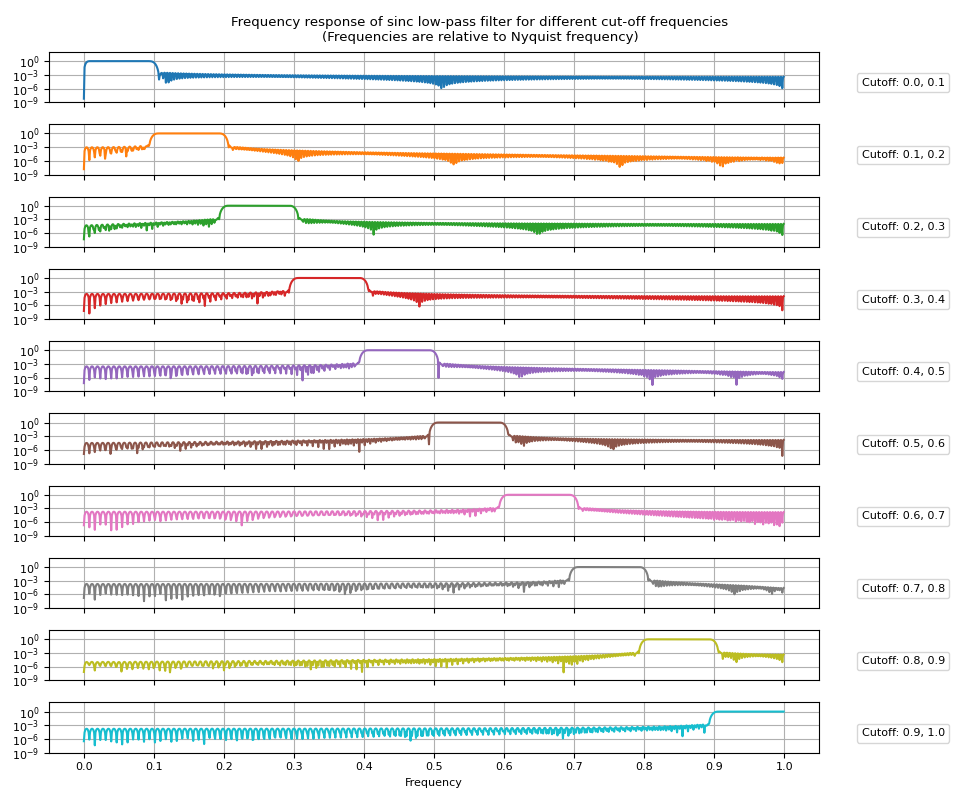
频率响应¶
频率采样¶
我们研究的下一种方法从期望的频率响应开始,并通过应用傅里叶逆变换获得脉冲响应。
frequency_impulse_response()接受频率的(未归一化)幅度分布并从中构建脉冲响应。
但请注意,生成的脉冲响应不会产生期望的频率响应。
在下文中,我们将创建多个滤波器并比较输入频率响应和实际频率响应。
砖墙滤波器¶
让我们从砖墙滤波器开始
magnitudes = torch.concat([torch.ones((128,)), torch.zeros((128,))])
ir = frequency_impulse_response(magnitudes)
print("Magnitudes:", magnitudes.shape)
print("Impulse Response:", ir.shape)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/filter_design_tutorial.py:258: UserWarning: torchaudio.prototype.functional._dsp.frequency_impulse_response has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
ir = frequency_impulse_response(magnitudes)
Magnitudes: torch.Size([256])
Impulse Response: torch.Size([510])
def plot_ir(magnitudes, ir, num_fft=2048):
fr = torch.fft.rfft(ir, n=num_fft, dim=0).abs()
ir_size = ir.size(-1)
half = ir_size // 2
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 1)
t = torch.linspace(-half, half - 1, ir_size)
axes[0].plot(t, ir)
axes[0].grid(True)
axes[0].set(title="Impulse Response")
axes[0].set_xticks([i * half // 4 for i in range(-4, 5)])
t = torch.linspace(0, 1, fr.numel())
axes[1].plot(t, fr, label="Actual")
axes[2].semilogy(t, fr, label="Actual")
t = torch.linspace(0, 1, magnitudes.numel())
for i in range(1, 3):
axes[i].plot(t, magnitudes, label="Desired (input)", linewidth=1.1, linestyle="--")
axes[i].grid(True)
axes[1].set(title="Frequency Response")
axes[2].set(title="Frequency Response (log-scale)", xlabel="Frequency")
axes[2].legend(loc="center right")
fig.tight_layout()
plot_ir(magnitudes, ir)
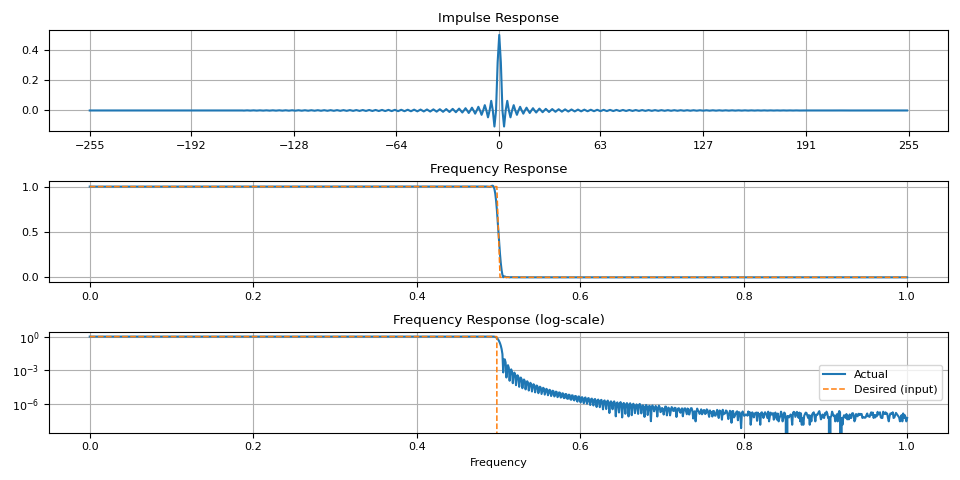
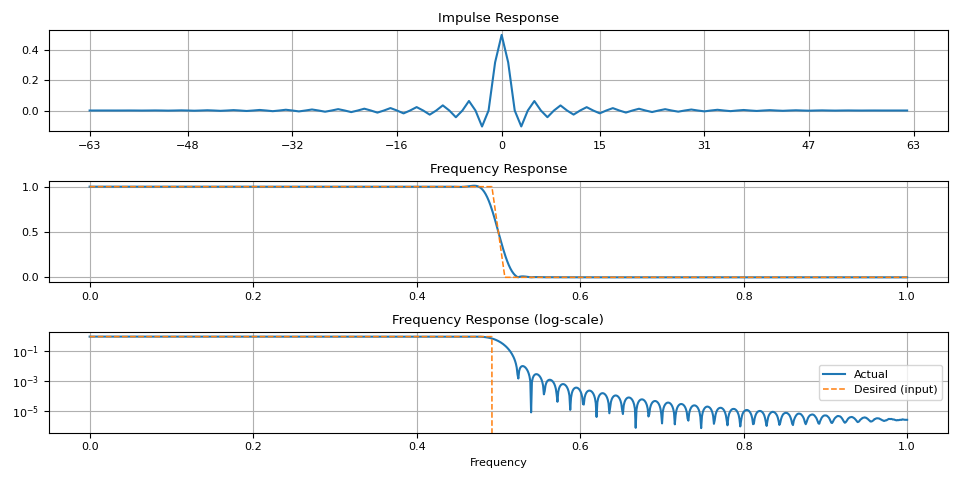
请注意,在过渡带附近存在伪影。当窗函数大小较小时,这一点更为明显。
magnitudes = torch.concat([torch.ones((32,)), torch.zeros((32,))])
ir = frequency_impulse_response(magnitudes)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/filter_design_tutorial.py:304: UserWarning: torchaudio.prototype.functional._dsp.frequency_impulse_response has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
ir = frequency_impulse_response(magnitudes)
plot_ir(magnitudes, ir)
任意形状¶
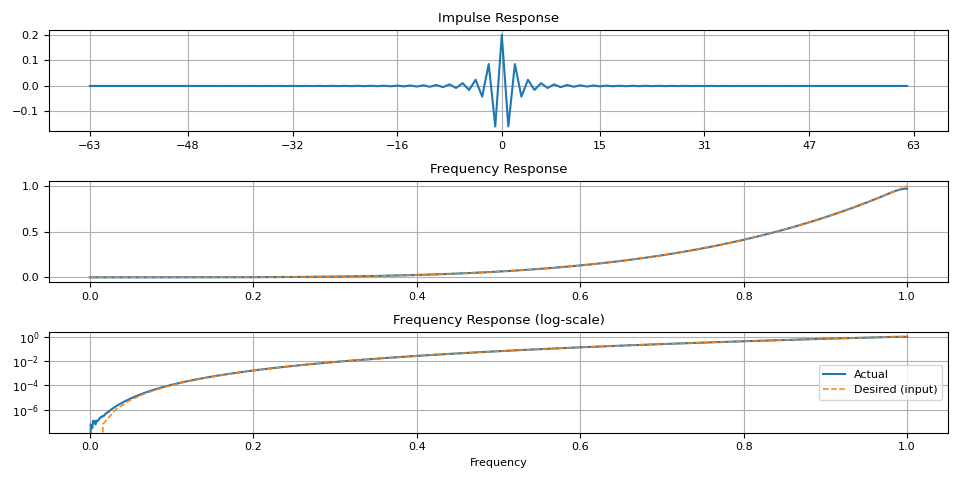
magnitudes = torch.linspace(0, 1, 64) ** 4.0
ir = frequency_impulse_response(magnitudes)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/filter_design_tutorial.py:319: UserWarning: torchaudio.prototype.functional._dsp.frequency_impulse_response has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
ir = frequency_impulse_response(magnitudes)
plot_ir(magnitudes, ir)
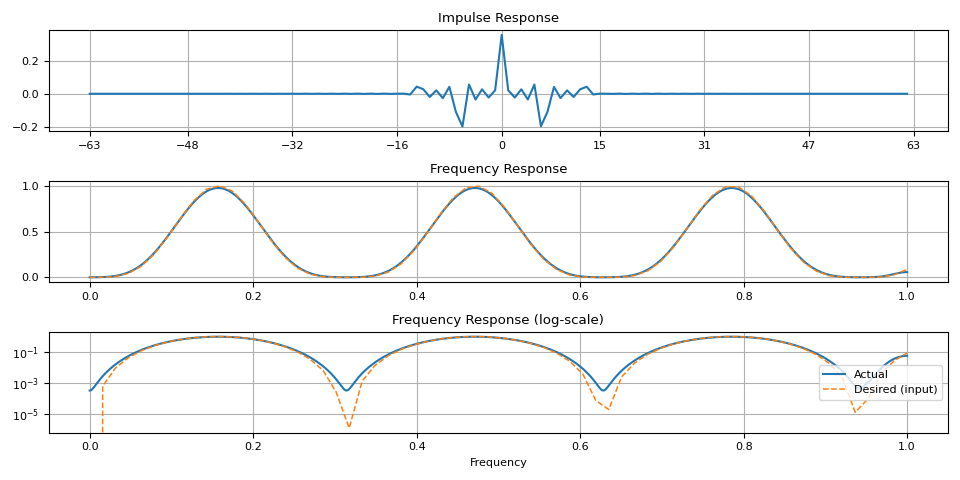
magnitudes = torch.sin(torch.linspace(0, 10, 64)) ** 4.0
ir = frequency_impulse_response(magnitudes)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/filter_design_tutorial.py:330: UserWarning: torchaudio.prototype.functional._dsp.frequency_impulse_response has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
ir = frequency_impulse_response(magnitudes)
plot_ir(magnitudes, ir)
参考资料¶
https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/dsp-book/dsp_book_Ch16.pdf
https://courses.engr.illinois.edu/ece401/fa2020/slides/lec10.pdf
https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~jos/sasp/Windowing_Desired_Impulse_Response.html
脚本总运行时间: ( 0 分 5.016 秒)



