注意
点击此处下载完整示例代码
使用 NVENC 加速视频编码¶
作者:Moto Hira
警告
从 2.8 版本开始,我们正在重构 TorchAudio,以使其进入维护阶段。因此:
本教程中描述的 API 在 2.8 版本中已被弃用,并将在 2.9 版本中移除。
PyTorch 用于音频和视频的解码和编码功能正在被整合到 TorchCodec 中。
请参阅 https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 获取更多信息。
本教程展示了如何使用 NVIDIA 的硬件视频编码器 (NVENC) 配合 TorchAudio,以及它如何提高视频编码性能。
注意
大多数现代 GPU 都同时拥有硬件解码器和编码器,但某些高端 GPU(如 A100 和 H100)没有硬件编码器。有关可用性和格式覆盖范围,请参阅以下链接:https://developer.nvidia.com/video-encode-and-decode-gpu-support-matrix-new
尝试在这些 GPU 上使用硬件编码器将失败,并显示类似外部库中的通用错误的错误消息。您可以通过torchaudio.utils.ffmpeg_utils.set_log_level()启用调试日志,以查看在此过程中发出的更详细的错误消息。
import torch
import torchaudio
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
import io
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import Video
from torchaudio.io import StreamReader, StreamWriter
2.8.0+cu126
2.8.0
检查先决条件¶
首先,我们检查 TorchAudio 是否正确检测到支持硬件解码器/编码器的 FFmpeg 库。
from torchaudio.utils import ffmpeg_utils
FFmpeg Library versions:
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:76: UserWarning: torio.utils.ffmpeg_utils.get_versions has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
for k, ver in ffmpeg_utils.get_versions().items():
libavcodec: 60.3.100
libavdevice: 60.1.100
libavfilter: 9.3.100
libavformat: 60.3.100
libavutil: 58.2.100
Available NVENC Encoders:
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:82: UserWarning: torio.utils.ffmpeg_utils.get_video_encoders has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
for k in ffmpeg_utils.get_video_encoders().keys():
- av1_nvenc
- h264_nvenc
- hevc_nvenc
print("Avaialbe GPU:")
print(torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0))
Avaialbe GPU:
_CudaDeviceProperties(name='NVIDIA A10G', major=8, minor=6, total_memory=22598MB, multi_processor_count=80, uuid=566db26d-0405-a011-4198-2699df443f87, pci_bus_id=0, pci_device_id=30, pci_domain_id=0, L2_cache_size=6MB)
我们使用以下辅助函数来生成测试帧数据。有关合成视频生成的详细信息,请参阅StreamReader 高级用法。
def get_data(height, width, format="yuv444p", frame_rate=30000 / 1001, duration=4):
src = f"testsrc2=rate={frame_rate}:size={width}x{height}:duration={duration}"
s = StreamReader(src=src, format="lavfi")
s.add_basic_video_stream(-1, format=format)
s.process_all_packets()
(video,) = s.pop_chunks()
return video
使用 NVENC 编码视频¶
要使用硬件视频编码器,您需要在定义输出视频流时,通过向add_video_stream()提供encoder选项来指定硬件编码器。
pict_config = {
"height": 360,
"width": 640,
"frame_rate": 30000 / 1001,
"format": "yuv444p",
}
frame_data = get_data(**pict_config)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:101: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src=src, format="lavfi")
w = StreamWriter(io.BytesIO(), format="mp4")
w.add_video_stream(**pict_config, encoder="h264_nvenc", encoder_format="yuv444p")
with w.open():
w.write_video_chunk(0, frame_data)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:132: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_encoder.StreamingMediaEncoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
w = StreamWriter(io.BytesIO(), format="mp4")
与硬件解码器类似,默认情况下,编码器期望帧数据位于 CPU 内存中。要从 CUDA 内存发送数据,您需要指定hw_accel选项。
buffer = io.BytesIO()
w = StreamWriter(buffer, format="mp4")
w.add_video_stream(**pict_config, encoder="h264_nvenc", encoder_format="yuv444p", hw_accel="cuda:0")
with w.open():
w.write_video_chunk(0, frame_data.to(torch.device("cuda:0")))
buffer.seek(0)
video_cuda = buffer.read()
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:144: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_encoder.StreamingMediaEncoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
w = StreamWriter(buffer, format="mp4")
Video(video_cuda, embed=True, mimetype="video/mp4")
使用 StreamWriter 对 NVENC 进行基准测试¶
现在我们比较软件编码器和硬件编码器的性能。
与 NVDEC 中的基准测试类似,我们处理不同分辨率的视频,并测量编码它们所需的时间。
我们还测量生成视频文件的大小。
以下函数编码给定的帧并测量编码所需的时间以及生成视频数据的大小。
def test_encode(data, encoder, width, height, hw_accel=None, **config):
assert data.is_cuda
buffer = io.BytesIO()
s = StreamWriter(buffer, format="mp4")
s.add_video_stream(encoder=encoder, width=width, height=height, hw_accel=hw_accel, **config)
with s.open():
t0 = time.monotonic()
if hw_accel is None:
data = data.to("cpu")
s.write_video_chunk(0, data)
elapsed = time.monotonic() - t0
size = buffer.tell()
fps = len(data) / elapsed
print(f" - Processed {len(data)} frames in {elapsed:.2f} seconds. ({fps:.2f} fps)")
print(f" - Encoded data size: {size} bytes")
return elapsed, size
我们对以下配置进行测试
软件编码器,线程数分别为 1、4、8
使用和不使用
hw_accel选项的硬件编码器。
def run_tests(height, width, duration=4):
# Generate the test data
print(f"Testing resolution: {width}x{height}")
pict_config = {
"height": height,
"width": width,
"frame_rate": 30000 / 1001,
"format": "yuv444p",
}
data = get_data(**pict_config, duration=duration)
data = data.to(torch.device("cuda:0"))
times = []
sizes = []
# Test software encoding
encoder_config = {
"encoder": "libx264",
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
}
for i, num_threads in enumerate([1, 4, 8]):
print(f"* Software Encoder (num_threads={num_threads})")
time_, size = test_encode(
data,
encoder_option={"threads": str(num_threads)},
**pict_config,
**encoder_config,
)
times.append(time_)
if i == 0:
sizes.append(size)
# Test hardware encoding
encoder_config = {
"encoder": "h264_nvenc",
"encoder_format": "yuv444p",
"encoder_option": {"gpu": "0"},
}
for i, hw_accel in enumerate([None, "cuda"]):
print(f"* Hardware Encoder {'(CUDA frames)' if hw_accel else ''}")
time_, size = test_encode(
data,
**pict_config,
**encoder_config,
hw_accel=hw_accel,
)
times.append(time_)
if i == 0:
sizes.append(size)
return times, sizes
我们更改视频分辨率以查看这些测量值如何变化。
360P¶
Testing resolution: 640x360
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:101: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src=src, format="lavfi")
* Software Encoder (num_threads=1)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:178: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_encoder.StreamingMediaEncoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamWriter(buffer, format="mp4")
- Processed 120 frames in 0.62 seconds. (192.36 fps)
- Encoded data size: 381331 bytes
* Software Encoder (num_threads=4)
- Processed 120 frames in 0.24 seconds. (501.65 fps)
- Encoded data size: 381307 bytes
* Software Encoder (num_threads=8)
- Processed 120 frames in 0.18 seconds. (672.48 fps)
- Encoded data size: 390689 bytes
* Hardware Encoder
- Processed 120 frames in 0.05 seconds. (2264.57 fps)
- Encoded data size: 1262979 bytes
* Hardware Encoder (CUDA frames)
- Processed 120 frames in 0.05 seconds. (2583.08 fps)
- Encoded data size: 1262979 bytes
720P¶
Testing resolution: 1280x720
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:101: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src=src, format="lavfi")
* Software Encoder (num_threads=1)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:178: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_encoder.StreamingMediaEncoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamWriter(buffer, format="mp4")
- Processed 120 frames in 2.31 seconds. (51.94 fps)
- Encoded data size: 1335451 bytes
* Software Encoder (num_threads=4)
- Processed 120 frames in 0.94 seconds. (128.08 fps)
- Encoded data size: 1336418 bytes
* Software Encoder (num_threads=8)
- Processed 120 frames in 0.88 seconds. (136.99 fps)
- Encoded data size: 1344063 bytes
* Hardware Encoder
- Processed 120 frames in 0.33 seconds. (367.70 fps)
- Encoded data size: 1358969 bytes
* Hardware Encoder (CUDA frames)
- Processed 120 frames in 0.15 seconds. (801.61 fps)
- Encoded data size: 1358969 bytes
1080P¶
Testing resolution: 1920x1080
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:101: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src=src, format="lavfi")
* Software Encoder (num_threads=1)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvenc_tutorial.py:178: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_encoder.StreamingMediaEncoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamWriter(buffer, format="mp4")
- Processed 120 frames in 4.77 seconds. (25.18 fps)
- Encoded data size: 2678241 bytes
* Software Encoder (num_threads=4)
- Processed 120 frames in 1.84 seconds. (65.11 fps)
- Encoded data size: 2682028 bytes
* Software Encoder (num_threads=8)
- Processed 120 frames in 1.71 seconds. (70.31 fps)
- Encoded data size: 2685086 bytes
* Hardware Encoder
- Processed 120 frames in 0.72 seconds. (166.12 fps)
- Encoded data size: 1705900 bytes
* Hardware Encoder (CUDA frames)
- Processed 120 frames in 0.32 seconds. (370.92 fps)
- Encoded data size: 1705900 bytes
现在我们绘制结果。
def plot():
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True, figsize=[9.6, 7.2])
for items in zip(time_360, time_720, time_1080, "ov^X+"):
axes[0].plot(items[:-1], marker=items[-1])
axes[0].grid(axis="both")
axes[0].set_xticks([0, 1, 2], ["360p", "720p", "1080p"], visible=True)
axes[0].tick_params(labeltop=False)
axes[0].legend(
[
"Software Encoding (threads=1)",
"Software Encoding (threads=4)",
"Software Encoding (threads=8)",
"Hardware Encoding (CPU Tensor)",
"Hardware Encoding (CUDA Tensor)",
]
)
axes[0].set_title("Time to encode videos with different resolutions")
axes[0].set_ylabel("Time [s]")
for items in zip(size_360, size_720, size_1080, "v^"):
axes[1].plot(items[:-1], marker=items[-1])
axes[1].grid(axis="both")
axes[1].set_xticks([0, 1, 2], ["360p", "720p", "1080p"])
axes[1].set_ylabel("The encoded size [bytes]")
axes[1].set_title("The size of encoded videos")
axes[1].legend(
[
"Software Encoding",
"Hardware Encoding",
]
)
plt.tight_layout()
plot()
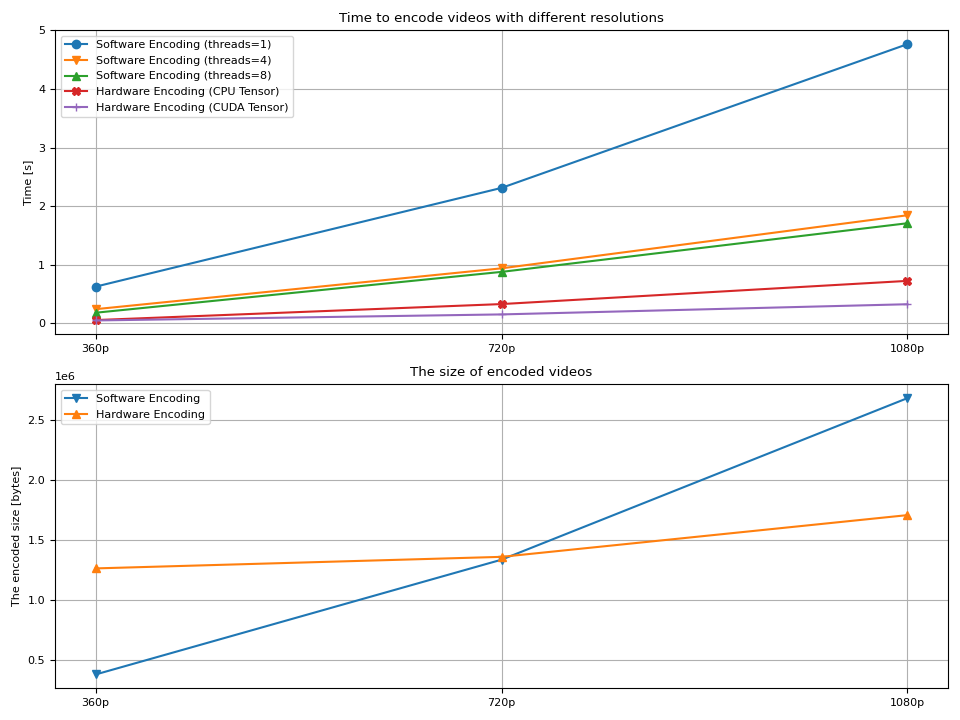
结果¶
我们观察到几件事;
编码视频的时间随着分辨率的增大而增加。
在软件编码的情况下,增加线程数有助于减少解码时间。
额外线程的增益在大约 8 个时开始减弱。
硬件编码通常比软件编码快。
使用
hw_accel本身并不能显著提高编码速度。生成视频的大小随着分辨率的增大而增大。
硬件编码器在更高分辨率下生成更小的视频文件。
最后一点对作者(非视频制作专家)来说有点奇怪。通常认为硬件解码器比软件编码器生成更大的视频。有人说软件编码器可以对编码配置进行细粒度控制,因此生成的视频更优化。同时,硬件编码器针对性能进行了优化,因此在质量和二进制大小方面没有提供太多控制。
质量抽查¶
那么,使用硬件编码器制作的视频质量如何?对高分辨率视频的快速抽查发现,它们在更高分辨率下有更明显的伪影。这可能是二进制文件较小的原因。(这意味着,它没有分配足够的比特来产生高质量的输出。)
以下图像是使用硬件编码器编码的视频的原始帧。
360P¶

720P¶

1080P¶
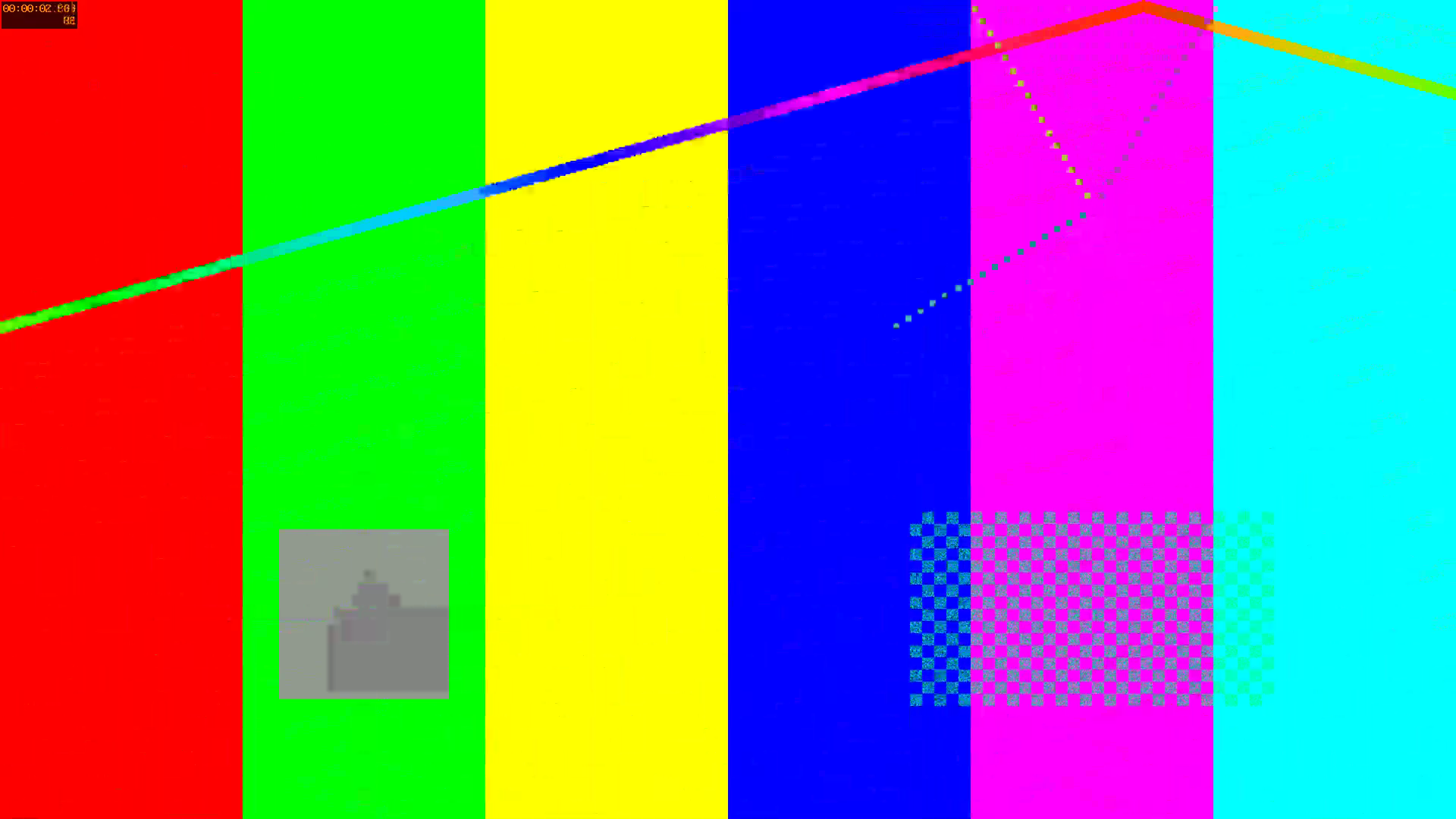

我们可以看到在更高分辨率下有更多明显的伪影。
也许可以使用encoder_options参数来减少这些伪影。我们没有尝试,但如果您尝试并找到更好的质量设置,请随时告诉我们。;)
脚本总运行时间: (0 分 23.330 秒)



