注意
点击此处下载完整示例代码
使用 NVDEC 加速视频解码¶
作者:Moto Hira
警告
从 2.8 版本开始,我们正在重构 TorchAudio,以使其进入维护阶段。因此:
本教程中描述的 API 在 2.8 版本中已被弃用,并将在 2.9 版本中移除。
PyTorch 用于音频和视频的解码和编码功能正在被整合到 TorchCodec 中。
请参阅 https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 获取更多信息。
本教程展示了如何将 NVIDIA 硬件视频解码器 (NVDEC) 与 TorchAudio 配合使用,以及它如何提高视频解码性能。
import torch
import torchaudio
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchaudio.__version__)
2.8.0+cu126
2.8.0
import os
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torchaudio.io import StreamReader
检查先决条件¶
首先,我们检查 TorchAudio 是否正确检测到支持硬件解码器/编码器的 FFmpeg 库。
from torchaudio.utils import ffmpeg_utils
FFmpeg Library versions:
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:64: UserWarning: torio.utils.ffmpeg_utils.get_versions has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
for k, ver in ffmpeg_utils.get_versions().items():
libavcodec: 60.3.100
libavdevice: 60.1.100
libavfilter: 9.3.100
libavformat: 60.3.100
libavutil: 58.2.100
Available NVDEC Decoders:
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:71: UserWarning: torio.utils.ffmpeg_utils.get_video_decoders has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
for k in ffmpeg_utils.get_video_decoders().keys():
- av1_cuvid
- h264_cuvid
- hevc_cuvid
- mjpeg_cuvid
- mpeg1_cuvid
- mpeg2_cuvid
- mpeg4_cuvid
- vc1_cuvid
- vp8_cuvid
- vp9_cuvid
print("Avaialbe GPU:")
print(torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0))
Avaialbe GPU:
_CudaDeviceProperties(name='NVIDIA A10G', major=8, minor=6, total_memory=22598MB, multi_processor_count=80, uuid=566db26d-0405-a011-4198-2699df443f87, pci_bus_id=0, pci_device_id=30, pci_domain_id=0, L2_cache_size=6MB)
我们将使用具有以下属性的视频:
编解码器:H.264
分辨率:960x540
帧率:29.97
像素格式:YUV420P
src = torchaudio.utils.download_asset(
"tutorial-assets/stream-api/NASAs_Most_Scientifically_Complex_Space_Observatory_Requires_Precision-MP4_small.mp4"
)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:99: UserWarning: torchaudio.utils.download.download_asset has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
src = torchaudio.utils.download_asset(
0%| | 0.00/31.8M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
88%|########7 | 27.9M/31.8M [00:00<00:00, 291MB/s]
100%|##########| 31.8M/31.8M [00:00<00:00, 291MB/s]
使用 NVDEC 解码视频¶
要使用硬件视频解码器,您需要在定义输出视频流时通过将decoder选项传递给add_video_stream()方法来指定硬件解码器。
s = StreamReader(src)
s.add_video_stream(5, decoder="h264_cuvid")
s.fill_buffer()
(video,) = s.pop_chunks()
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:112: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
解码后的视频帧以 NCHW 格式的张量形式返回。
print(video.shape, video.dtype)
torch.Size([5, 3, 540, 960]) torch.uint8
默认情况下,解码后的帧发送回 CPU 内存,并创建 CPU 张量。
print(video.device)
cpu
通过指定hw_accel选项,您可以将解码后的帧转换为 CUDA 张量。hw_accel选项接受字符串值并将其传递给torch.device。
注意
目前,hw_accel选项和add_basic_video_stream()不兼容。add_basic_video_stream添加了解码后处理,该处理是为 CPU 内存中的帧设计的。请使用add_video_stream()。
s = StreamReader(src)
s.add_video_stream(5, decoder="h264_cuvid", hw_accel="cuda:0")
s.fill_buffer()
(video,) = s.pop_chunks()
print(video.shape, video.dtype, video.device)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:146: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
torch.Size([5, 3, 540, 960]) torch.uint8 cuda:0
注意
当有多个 GPU 可用时,StreamReader默认使用第一个 GPU。您可以通过提供"gpu"选项来更改此设置。
# Video data is sent to CUDA device 0, decoded and
# converted on the same device.
s.add_video_stream(
...,
decoder="h264_cuvid",
decoder_option={"gpu": "0"},
hw_accel="cuda:0",
)
注意
"gpu"选项和hw_accel选项可以独立指定。如果它们不匹配,解码后的帧将自动传输到hw_accell指定的设备。
# Video data is sent to CUDA device 0, and decoded there.
# Then it is transfered to CUDA device 1, and converted to
# CUDA tensor.
s.add_video_stream(
...,
decoder="h264_cuvid",
decoder_option={"gpu": "0"},
hw_accel="cuda:1",
)
可视化¶
让我们看看通过硬件解码器解码的帧,并将它们与软件解码器的等效结果进行比较。
以下函数会查找给定时间戳并使用指定的解码器解码一帧。
def test_decode(decoder: str, seek: float):
s = StreamReader(src)
s.seek(seek)
s.add_video_stream(1, decoder=decoder)
s.fill_buffer()
(video,) = s.pop_chunks()
return video[0]
timestamps = [12, 19, 45, 131, 180]
cpu_frames = [test_decode(decoder="h264", seek=ts) for ts in timestamps]
cuda_frames = [test_decode(decoder="h264_cuvid", seek=ts) for ts in timestamps]
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:203: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
注意
目前,硬件解码器不支持颜色空间转换。解码后的帧为 YUV 格式。以下函数执行 YUV 到 RGB 转换(以及用于绘图的轴混洗)。
def yuv_to_rgb(frames):
frames = frames.cpu().to(torch.float)
y = frames[..., 0, :, :]
u = frames[..., 1, :, :]
v = frames[..., 2, :, :]
y /= 255
u = u / 255 - 0.5
v = v / 255 - 0.5
r = y + 1.14 * v
g = y + -0.396 * u - 0.581 * v
b = y + 2.029 * u
rgb = torch.stack([r, g, b], -1)
rgb = (rgb * 255).clamp(0, 255).to(torch.uint8)
return rgb.numpy()
现在我们可视化结果。
def plot():
n_rows = len(timestamps)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(n_rows, 2, figsize=[12.8, 16.0])
for i in range(n_rows):
axes[i][0].imshow(yuv_to_rgb(cpu_frames[i]))
axes[i][1].imshow(yuv_to_rgb(cuda_frames[i]))
axes[0][0].set_title("Software decoder")
axes[0][1].set_title("HW decoder")
plt.setp(axes, xticks=[], yticks=[])
plt.tight_layout()
plot()
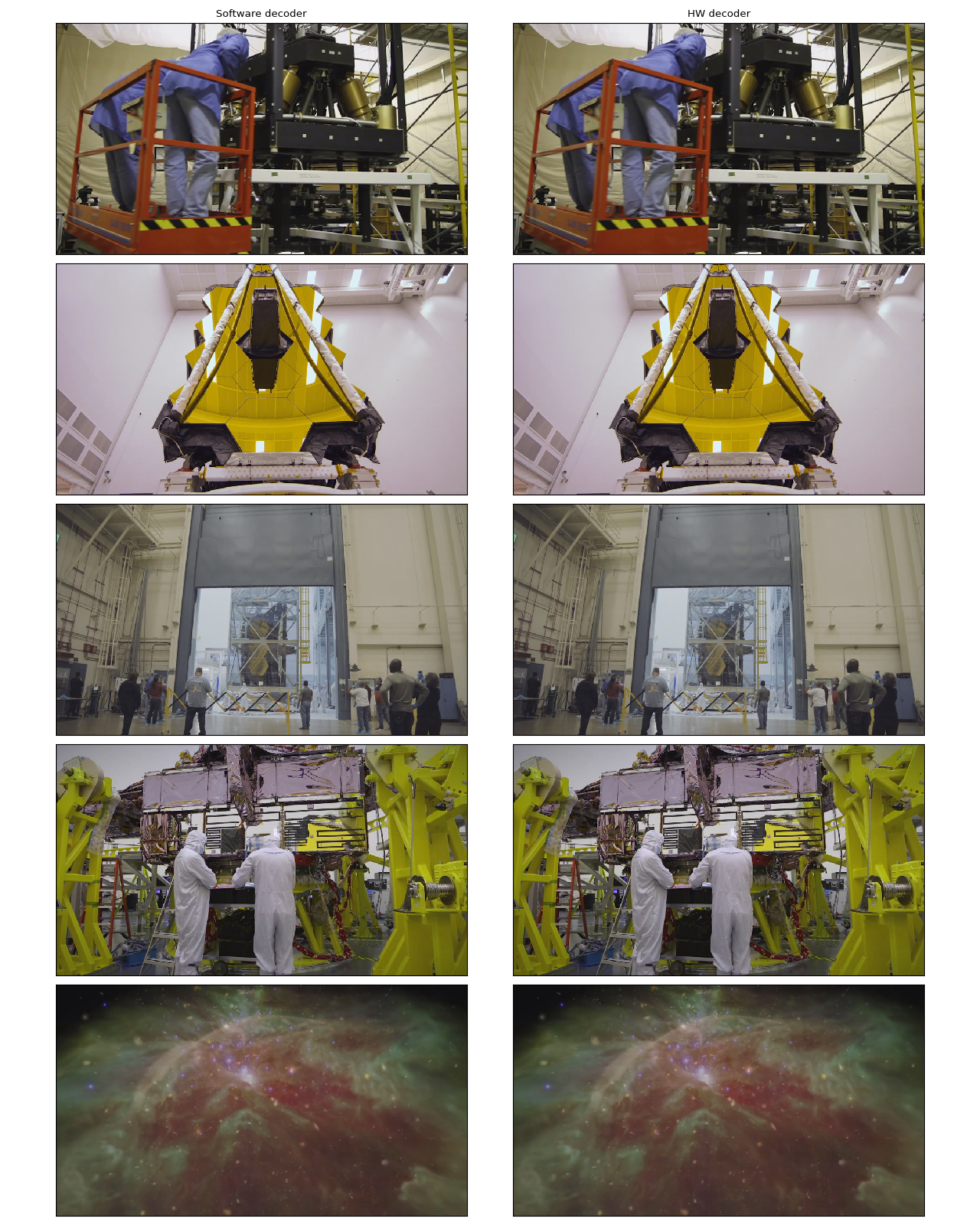
在作者看来,它们无法区分。如果您发现任何问题,请随时告诉我们。:)
硬件调整大小和裁剪¶
您可以使用decoder_option参数提供特定于解码器的选项。
以下选项通常与预处理相关。
resize:将帧调整为(width)x(height)。crop:裁剪帧(top)x(bottom)x(left)x(right)。请注意,指定的值是删除的行/列的数量。最终图像大小为(width - left - right)x(height - top -bottom)。如果同时使用crop和resize选项,则首先执行crop。
有关其他可用选项,请运行ffmpeg -h decoder=h264_cuvid。
def test_options(option):
s = StreamReader(src)
s.seek(87)
s.add_video_stream(1, decoder="h264_cuvid", hw_accel="cuda:0", decoder_option=option)
s.fill_buffer()
(video,) = s.pop_chunks()
print(f"Option: {option}:\t{video.shape}")
return video[0]
original = test_options(option=None)
resized = test_options(option={"resize": "480x270"})
cropped = test_options(option={"crop": "135x135x240x240"})
cropped_and_resized = test_options(option={"crop": "135x135x240x240", "resize": "640x360"})
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:298: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
Option: None: torch.Size([1, 3, 540, 960])
Option: {'resize': '480x270'}: torch.Size([1, 3, 270, 480])
Option: {'crop': '135x135x240x240'}: torch.Size([1, 3, 270, 480])
Option: {'crop': '135x135x240x240', 'resize': '640x360'}: torch.Size([1, 3, 360, 640])
def plot():
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=[12.8, 9.6])
axes[0][0].imshow(yuv_to_rgb(original))
axes[0][1].imshow(yuv_to_rgb(resized))
axes[1][0].imshow(yuv_to_rgb(cropped))
axes[1][1].imshow(yuv_to_rgb(cropped_and_resized))
axes[0][0].set_title("Original")
axes[0][1].set_title("Resized")
axes[1][0].set_title("Cropped")
axes[1][1].set_title("Cropped and resized")
plt.tight_layout()
return fig
plot()
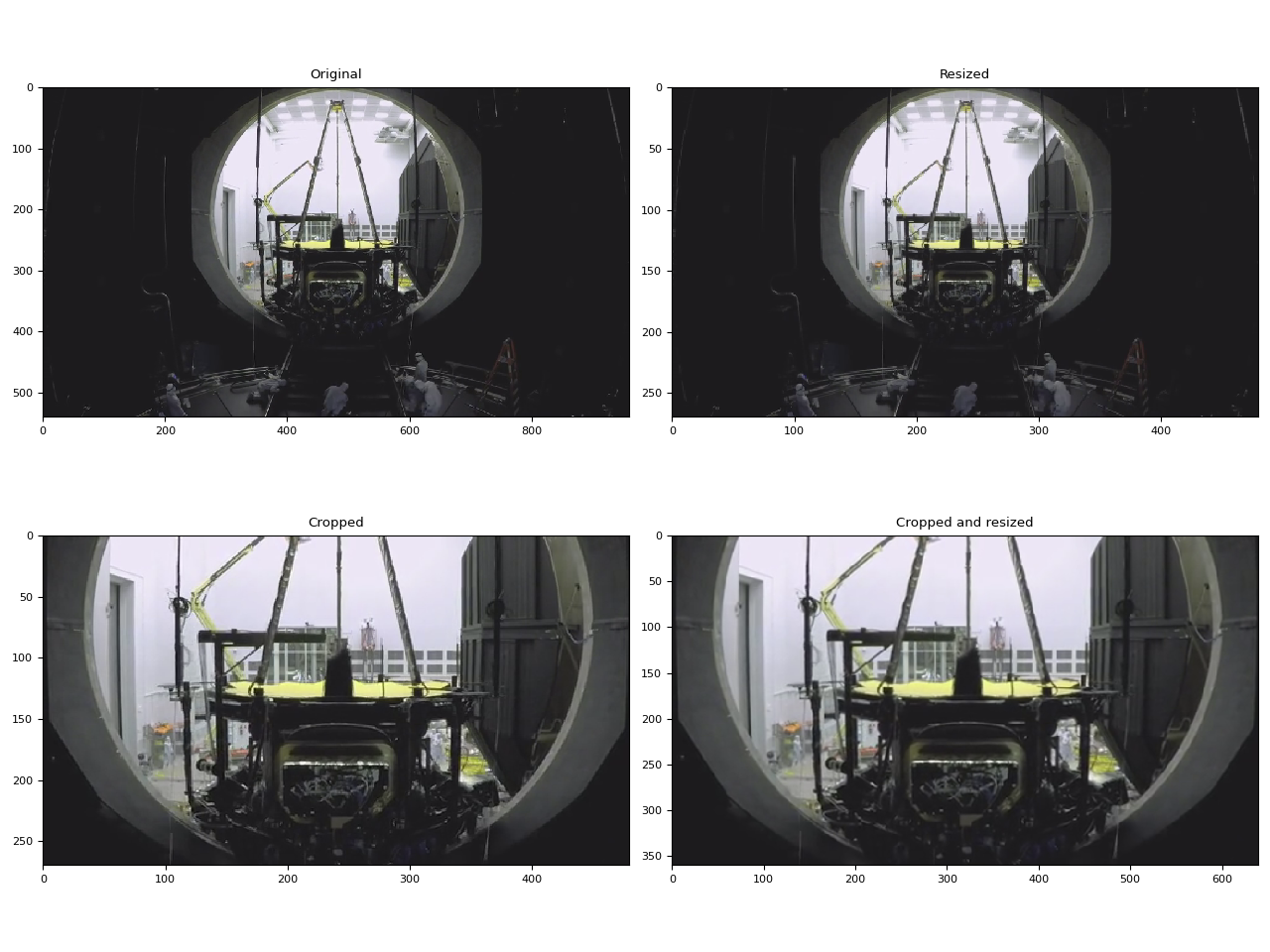
<Figure size 1280x960 with 4 Axes>
比较调整大小方法¶
与软件缩放不同,NVDEC 不提供选择缩放算法的选项。在 ML 应用程序中,通常需要构建具有相似数值属性的预处理管道。因此,我们在此处比较硬件调整大小与不同算法的软件调整大小的结果。
我们将使用以下视频,其中包含使用以下命令生成的测试模式。
ffmpeg -y -f lavfi -t 12.05 -i mptestsrc -movflags +faststart mptestsrc.mp4
test_src = torchaudio.utils.download_asset("tutorial-assets/mptestsrc.mp4")
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:365: UserWarning: torchaudio.utils.download.download_asset has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
test_src = torchaudio.utils.download_asset("tutorial-assets/mptestsrc.mp4")
0%| | 0.00/232k [00:00<?, ?B/s]
100%|##########| 232k/232k [00:00<00:00, 128MB/s]
以下函数解码视频并应用指定的缩放算法。
def decode_resize_ffmpeg(mode, height, width, seek):
filter_desc = None if mode is None else f"scale={width}:{height}:sws_flags={mode}"
s = StreamReader(test_src)
s.add_video_stream(1, filter_desc=filter_desc)
s.seek(seek)
s.fill_buffer()
(chunk,) = s.pop_chunks()
return chunk
以下函数使用硬件解码器解码视频并调整大小。
def decode_resize_cuvid(height, width, seek):
s = StreamReader(test_src)
s.add_video_stream(1, decoder="h264_cuvid", decoder_option={"resize": f"{width}x{height}"}, hw_accel="cuda:0")
s.seek(seek)
s.fill_buffer()
(chunk,) = s.pop_chunks()
return chunk.cpu()
现在我们执行它们并可视化结果帧。
params = {"height": 224, "width": 224, "seek": 3}
frames = [
decode_resize_ffmpeg(None, **params),
decode_resize_ffmpeg("neighbor", **params),
decode_resize_ffmpeg("bilinear", **params),
decode_resize_ffmpeg("bicubic", **params),
decode_resize_cuvid(**params),
decode_resize_ffmpeg("spline", **params),
decode_resize_ffmpeg("lanczos:param0=1", **params),
decode_resize_ffmpeg("lanczos:param0=3", **params),
decode_resize_ffmpeg("lanczos:param0=5", **params),
]
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:376: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(test_src)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:390: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(test_src)
def plot():
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 3, figsize=[12.8, 15.2])
for i, f in enumerate(frames):
h, w = f.shape[2:4]
f = f[..., : h // 4, : w // 4]
axes[i // 3][i % 3].imshow(yuv_to_rgb(f[0]))
axes[0][0].set_title("Original")
axes[0][1].set_title("nearest neighbor")
axes[0][2].set_title("bilinear")
axes[1][0].set_title("bicubic")
axes[1][1].set_title("NVDEC")
axes[1][2].set_title("spline")
axes[2][0].set_title("lanczos(1)")
axes[2][1].set_title("lanczos(3)")
axes[2][2].set_title("lanczos(5)")
plt.setp(axes, xticks=[], yticks=[])
plt.tight_layout()
plot()
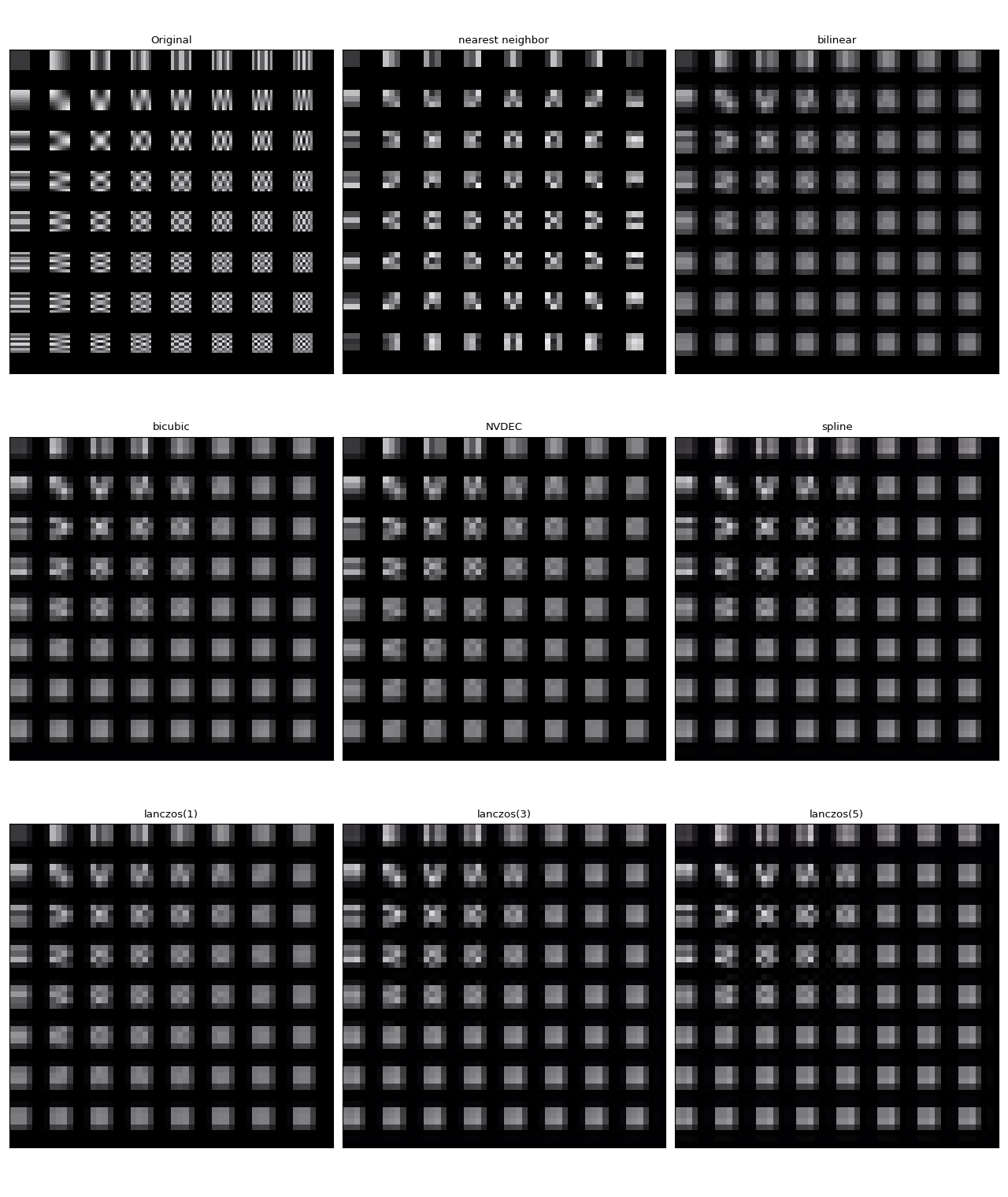
它们都不完全相同。在作者看来,lanczos(1) 看起来与 NVDEC 最相似。双三次插值也看起来很接近。
使用 StreamReader 对 NVDEC 进行基准测试¶
在本节中,我们比较软件视频解码和硬件视频解码的性能。
解码为 CUDA 帧¶
首先,我们比较软件解码器和硬件编码器解码同一视频所需的时间。为了使结果具有可比性,当使用软件解码器时,我们将结果张量移动到 CUDA。
测试过程如下所示:
使用硬件解码器并直接将数据放置在 CUDA 上
使用软件解码器,生成 CPU 张量并将其移动到 CUDA。
以下函数实现硬件解码器测试用例。
def test_decode_cuda(src, decoder, hw_accel="cuda", frames_per_chunk=5):
s = StreamReader(src)
s.add_video_stream(frames_per_chunk, decoder=decoder, hw_accel=hw_accel)
num_frames = 0
chunk = None
t0 = time.monotonic()
for (chunk,) in s.stream():
num_frames += chunk.shape[0]
elapsed = time.monotonic() - t0
print(f" - Shape: {chunk.shape}")
fps = num_frames / elapsed
print(f" - Processed {num_frames} frames in {elapsed:.2f} seconds. ({fps:.2f} fps)")
return fps
以下函数实现软件解码器测试用例。
def test_decode_cpu(src, threads, decoder=None, frames_per_chunk=5):
s = StreamReader(src)
s.add_video_stream(frames_per_chunk, decoder=decoder, decoder_option={"threads": f"{threads}"})
num_frames = 0
device = torch.device("cuda")
t0 = time.monotonic()
for i, (chunk,) in enumerate(s.stream()):
if i == 0:
print(f" - Shape: {chunk.shape}")
num_frames += chunk.shape[0]
chunk = chunk.to(device)
elapsed = time.monotonic() - t0
fps = num_frames / elapsed
print(f" - Processed {num_frames} frames in {elapsed:.2f} seconds. ({fps:.2f} fps)")
return fps
对于每个分辨率的视频,我们运行多个软件解码器测试用例,线程数不同。
def run_decode_tests(src, frames_per_chunk=5):
fps = []
print(f"Testing: {os.path.basename(src)}")
for threads in [1, 4, 8, 16]:
print(f"* Software decoding (num_threads={threads})")
fps.append(test_decode_cpu(src, threads))
print("* Hardware decoding")
fps.append(test_decode_cuda(src, decoder="h264_cuvid"))
return fps
现在我们使用不同分辨率的视频运行测试。
QVGA¶
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:542: UserWarning: torchaudio.utils.download.download_asset has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
src_qvga = torchaudio.utils.download_asset("tutorial-assets/testsrc2_qvga.h264.mp4")
0%| | 0.00/1.06M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
100%|##########| 1.06M/1.06M [00:00<00:00, 267MB/s]
Testing: testsrc2_qvga.h264.mp4
* Software decoding (num_threads=1)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:503: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 240, 320])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.50 seconds. (1792.93 fps)
* Software decoding (num_threads=4)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 240, 320])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.35 seconds. (2551.90 fps)
* Software decoding (num_threads=8)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 240, 320])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.34 seconds. (2662.90 fps)
* Software decoding (num_threads=16)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 240, 320])
- Processed 895 frames in 0.35 seconds. (2551.38 fps)
* Hardware decoding
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:483: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 240, 320])
- Processed 900 frames in 2.01 seconds. (447.51 fps)
VGA¶
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:549: UserWarning: torchaudio.utils.download.download_asset has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
src_vga = torchaudio.utils.download_asset("tutorial-assets/testsrc2_vga.h264.mp4")
0%| | 0.00/3.59M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
100%|##########| 3.59M/3.59M [00:00<00:00, 407MB/s]
Testing: testsrc2_vga.h264.mp4
* Software decoding (num_threads=1)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:503: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 480, 640])
- Processed 900 frames in 1.26 seconds. (711.65 fps)
* Software decoding (num_threads=4)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 480, 640])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.69 seconds. (1302.73 fps)
* Software decoding (num_threads=8)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 480, 640])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.73 seconds. (1239.85 fps)
* Software decoding (num_threads=16)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 480, 640])
- Processed 895 frames in 0.66 seconds. (1353.78 fps)
* Hardware decoding
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:483: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 480, 640])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.34 seconds. (2639.67 fps)
XGA¶
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:556: UserWarning: torchaudio.utils.download.download_asset has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
src_xga = torchaudio.utils.download_asset("tutorial-assets/testsrc2_xga.h264.mp4")
0%| | 0.00/9.22M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
100%|##########| 9.22M/9.22M [00:00<00:00, 319MB/s]
Testing: testsrc2_xga.h264.mp4
* Software decoding (num_threads=1)
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:503: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 768, 1024])
- Processed 900 frames in 2.68 seconds. (335.81 fps)
* Software decoding (num_threads=4)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 768, 1024])
- Processed 900 frames in 1.17 seconds. (771.75 fps)
* Software decoding (num_threads=8)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 768, 1024])
- Processed 900 frames in 1.07 seconds. (838.61 fps)
* Software decoding (num_threads=16)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 768, 1024])
- Processed 895 frames in 1.01 seconds. (881.89 fps)
* Hardware decoding
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:483: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 768, 1024])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.61 seconds. (1473.41 fps)
结果¶
现在我们绘制结果。
def plot():
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=[9.6, 6.4])
for items in zip(fps_qvga, fps_vga, fps_xga, "ov^sx"):
ax.plot(items[:-1], marker=items[-1])
ax.grid(axis="both")
ax.set_xticks([0, 1, 2], ["QVGA (320x240)", "VGA (640x480)", "XGA (1024x768)"])
ax.legend(
[
"Software Decoding (threads=1)",
"Software Decoding (threads=4)",
"Software Decoding (threads=8)",
"Software Decoding (threads=16)",
"Hardware Decoding (CUDA Tensor)",
]
)
ax.set_title("Speed of processing video frames")
ax.set_ylabel("Frames per second")
plt.tight_layout()
plot()
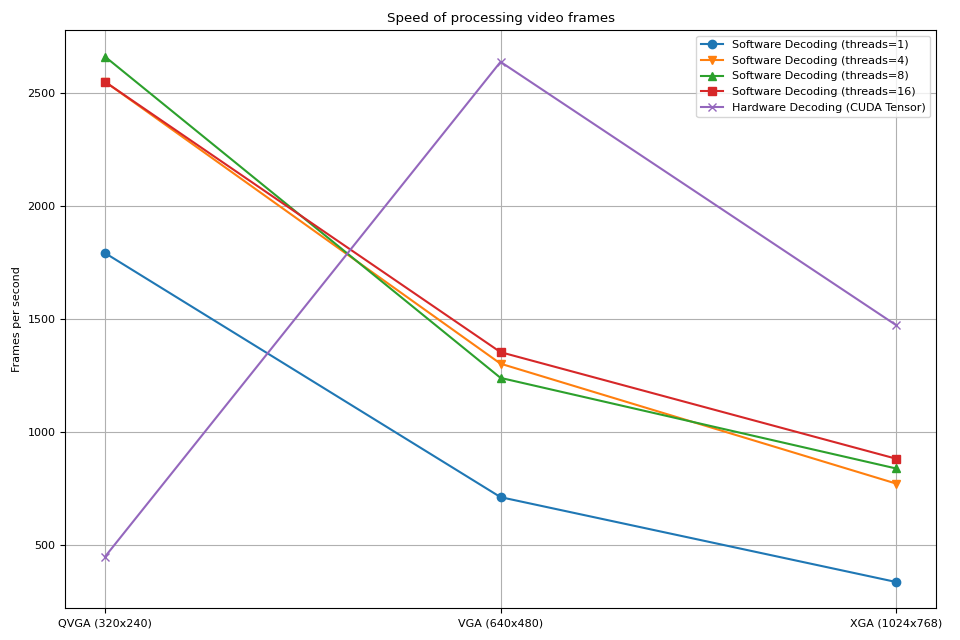
我们观察到几件事:
增加软件解码中的线程数会加快管道速度,但性能在大约 8 个线程时达到饱和。
使用硬件解码器带来的性能提升取决于视频的分辨率。
在 QVGA 等较低分辨率下,硬件解码比软件解码慢
在 XGA 等较高分辨率下,硬件解码比软件解码快。
值得注意的是,性能提升还取决于 GPU 类型。我们观察到,在使用 V100 或 A100 GPU 解码 VGA 视频时,硬件解码器比软件解码器慢。但使用 A10 GPU 硬件解码器比软件解码器快。
解码和调整大小¶
接下来,我们将调整大小操作添加到管道中。我们将比较以下管道。
使用软件解码器解码视频并以 PyTorch 张量读取帧。使用
torch.nn.functional.interpolate()调整张量大小,然后将结果张量发送到 CUDA 设备。使用软件解码器解码视频,使用 FFmpeg 的滤镜图调整帧大小,以 PyTorch 张量读取调整大小的帧,然后将其发送到 CUDA 设备。
使用硬件解码器同时解码和调整视频大小,以 CUDA 张量读取结果帧。
管道 1 代表常见的视频加载实现。
管道 2 使用 FFmpeg 的滤镜图,它允许在将原始帧转换为张量之前对其进行操作。
管道 3 具有从 CPU 到 CUDA 的最小数据传输量,这显著有助于高性能数据加载。
以下函数实现管道 1。它使用 PyTorch 的torch.nn.functional.interpolate()。我们使用bincubic模式,因为我们发现结果帧最接近 NVDEC 调整大小。
def test_decode_then_resize(src, height, width, mode="bicubic", frames_per_chunk=5):
s = StreamReader(src)
s.add_video_stream(frames_per_chunk, decoder_option={"threads": "8"})
num_frames = 0
device = torch.device("cuda")
chunk = None
t0 = time.monotonic()
for (chunk,) in s.stream():
num_frames += chunk.shape[0]
chunk = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(chunk, [height, width], mode=mode, antialias=True)
chunk = chunk.to(device)
elapsed = time.monotonic() - t0
fps = num_frames / elapsed
print(f" - Shape: {chunk.shape}")
print(f" - Processed {num_frames} frames in {elapsed:.2f} seconds. ({fps:.2f} fps)")
return fps
以下函数实现管道 2。帧作为解码过程的一部分进行调整大小,然后发送到 CUDA 设备。
我们使用bincubic模式,以使结果与上面基于 PyTorch 的实现具有可比性。
def test_decode_and_resize(src, height, width, mode="bicubic", frames_per_chunk=5):
s = StreamReader(src)
s.add_video_stream(
frames_per_chunk, filter_desc=f"scale={width}:{height}:sws_flags={mode}", decoder_option={"threads": "8"}
)
num_frames = 0
device = torch.device("cuda")
chunk = None
t0 = time.monotonic()
for (chunk,) in s.stream():
num_frames += chunk.shape[0]
chunk = chunk.to(device)
elapsed = time.monotonic() - t0
fps = num_frames / elapsed
print(f" - Shape: {chunk.shape}")
print(f" - Processed {num_frames} frames in {elapsed:.2f} seconds. ({fps:.2f} fps)")
return fps
以下函数实现管道 3。调整大小由 NVDEC 执行,结果张量放置在 CUDA 内存中。
def test_hw_decode_and_resize(src, decoder, decoder_option, hw_accel="cuda", frames_per_chunk=5):
s = StreamReader(src)
s.add_video_stream(5, decoder=decoder, decoder_option=decoder_option, hw_accel=hw_accel)
num_frames = 0
chunk = None
t0 = time.monotonic()
for (chunk,) in s.stream():
num_frames += chunk.shape[0]
elapsed = time.monotonic() - t0
fps = num_frames / elapsed
print(f" - Shape: {chunk.shape}")
print(f" - Processed {num_frames} frames in {elapsed:.2f} seconds. ({fps:.2f} fps)")
return fps
以下函数在给定源上运行基准测试函数。
def run_resize_tests(src):
print(f"Testing: {os.path.basename(src)}")
height, width = 224, 224
print("* Software decoding with PyTorch interpolate")
cpu_resize1 = test_decode_then_resize(src, height=height, width=width)
print("* Software decoding with FFmpeg scale")
cpu_resize2 = test_decode_and_resize(src, height=height, width=width)
print("* Hardware decoding with resize")
cuda_resize = test_hw_decode_and_resize(src, decoder="h264_cuvid", decoder_option={"resize": f"{width}x{height}"})
return [cpu_resize1, cpu_resize2, cuda_resize]
现在我们运行测试。
QVGA¶
Testing: testsrc2_qvga.h264.mp4
* Software decoding with PyTorch interpolate
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:647: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 224, 224])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.59 seconds. (1517.03 fps)
* Software decoding with FFmpeg scale
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:675: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 224, 224])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.38 seconds. (2391.42 fps)
* Hardware decoding with resize
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:700: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 224, 224])
- Processed 900 frames in 2.01 seconds. (447.62 fps)
VGA¶
Testing: testsrc2_vga.h264.mp4
* Software decoding with PyTorch interpolate
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:647: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 224, 224])
- Processed 900 frames in 1.36 seconds. (659.64 fps)
* Software decoding with FFmpeg scale
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:675: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 224, 224])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.68 seconds. (1333.05 fps)
* Hardware decoding with resize
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:700: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 224, 224])
- Processed 900 frames in 1.47 seconds. (611.88 fps)
XGA¶
Testing: testsrc2_xga.h264.mp4
* Software decoding with PyTorch interpolate
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:647: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 224, 224])
- Processed 900 frames in 2.55 seconds. (352.97 fps)
* Software decoding with FFmpeg scale
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:675: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 224, 224])
- Processed 900 frames in 1.06 seconds. (847.18 fps)
* Hardware decoding with resize
/pytorch/audio/examples/tutorials/nvdec_tutorial.py:700: UserWarning: torio.io._streaming_media_decoder.StreamingMediaDecoder has been deprecated. This deprecation is part of a large refactoring effort to transition TorchAudio into a maintenance phase. The decoding and encoding capabilities of PyTorch for both audio and video are being consolidated into TorchCodec. Please see https://github.com/pytorch/audio/issues/3902 for more information. It will be removed from the 2.9 release.
s = StreamReader(src)
- Shape: torch.Size([5, 3, 224, 224])
- Processed 900 frames in 0.61 seconds. (1480.00 fps)
结果¶
现在我们绘制结果。
def plot():
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=[9.6, 6.4])
for items in zip(fps_qvga, fps_vga, fps_xga, "ov^sx"):
ax.plot(items[:-1], marker=items[-1])
ax.grid(axis="both")
ax.set_xticks([0, 1, 2], ["QVGA (320x240)", "VGA (640x480)", "XGA (1024x768)"])
ax.legend(
[
"Software decoding\nwith resize\n(PyTorch interpolate)",
"Software decoding\nwith resize\n(FFmpeg scale)",
"NVDEC\nwith resizing",
]
)
ax.set_title("Speed of processing video frames")
ax.set_xlabel("Input video resolution")
ax.set_ylabel("Frames per second")
plt.tight_layout()
plot()
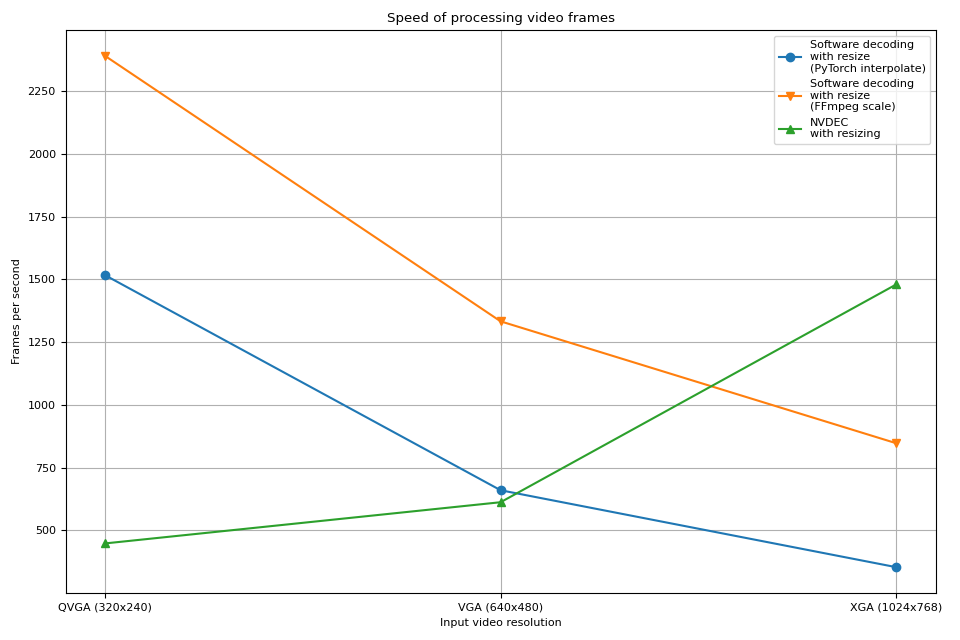
硬件解码器显示出与之前实验相似的趋势。事实上,性能几乎相同。硬件调整大小对于缩小帧几乎没有开销。
软件解码也显示出类似的趋势。将调整大小作为解码过程的一部分进行会更快。一种可能的解释是,视频帧在内部以 YUV420P 格式存储,其像素数量是 RGB24 或 YUV444P 的一半。这意味着如果在将帧数据复制到 PyTorch 张量之前进行调整大小,则操作和复制的像素数量小于在帧转换为张量后应用调整大小的情况。
脚本总运行时间:(0 分 30.874 秒)



