Dynamo 核心概念#
创建时间:2025 年 7 月 28 日 | 最后更新时间:2025 年 7 月 28 日
摘要
Dynamo 是
torch.compile的前端,它执行跟踪 (tracing) 以将 Python 函数(及其嵌套函数调用)的语义捕获到一系列线性操作(即“(FX) 图”)、剩余字节码和“守卫”(一组图和字节码有效的条件列表)。不支持的 Python 功能会导致图中断 (graph breaks),此时 Dynamo 会编译从跟踪中获得的局部图,然后执行不支持的代码,之后在不支持的代码之后恢复跟踪。
图中断可能导致 torch.compile 性能下降,并阻止后端优化机会。如果您未获得预期性能,请检查图中断。
Dynamo 跟踪#
torch.compile 的前端 (Dynamo) 是一个自定义的 Python 字节码解释器,旨在允许在 PyTorch 程序中进行图编译,同时保留 Python 的全部灵活性。给定一个要编译的函数,Dynamo 会解释 Python 字节码,将一系列 PyTorch 操作提取到 1 个或多个 FX 图中,这些图可以由后端进一步优化。
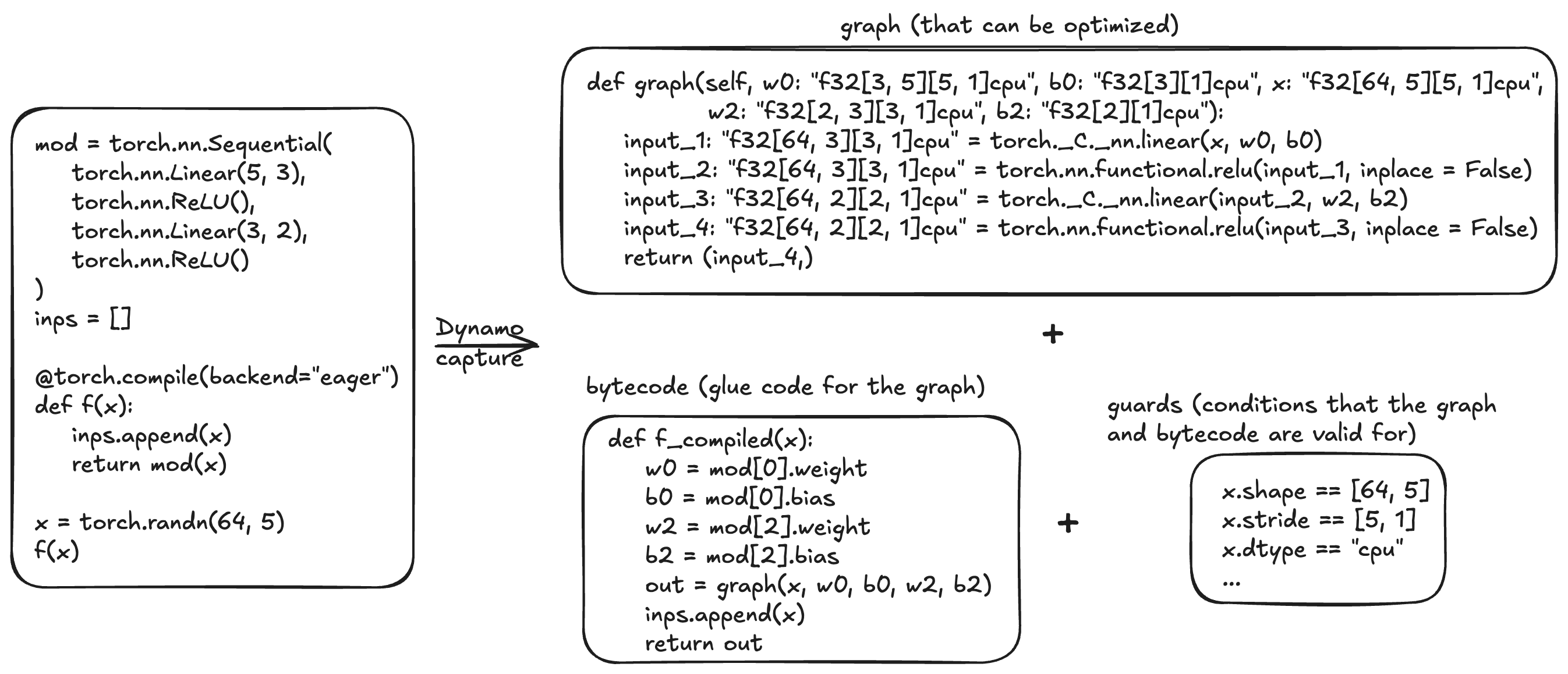
例如,对于上面图示中的函数 f,Dynamo 会生成
一个接受原始输入以及函数所需的其他一些输入的FX 图。
Python 字节码,可用作
f的直接替代。在我们的示例中,字节码会检索其他输入并将其传递给图,并且还包含无法优化的 Python 副作用(列表追加)。守卫 (guards),它们指定图和字节码有效的条件。除非另有说明,否则 Dynamo 生成的图会针对输入 Tensor 的形状进行专门化。
图中断#
Dynamo 会跟踪您的代码,并尝试将您的 PyTorch 代码捕获到一个 PyTorch 运算符的计算图中(FX 图)。然而,这并非总是可能的。当遇到无法跟踪的代码时,会发生“图中断 (graph break)”。在默认的 torch.compile 设置中,图中断包括编译到目前为止确定的 FX 图,在常规 Python 中运行不支持的代码,然后在新 FX 图中恢复跟踪。
图中断是一项功能,它允许 Dynamo 运行任意 Python 代码,并切分出可以单独优化的功能性子图。
但是,图中断可能会导致 torch.compile 出现意想不到的性能下降。如果您未获得预期的加速,我们建议您检查图中断并将其移除。
图中断可能发生在以下情况:
依赖数据的 if 语句
许多 Python 内置函数
C 函数
下面是一个由于调用不支持的操作 torch.save 而导致的图中断示例。
@torch.compile
def f(x):
y = x ** 2 / 2
torch.save(y, "foo.pt") # torch.save is an unsupported operation
z = y ** 3 / 6
return z
x = torch.randn(3)
print(f(x))
tensor([6.4034e-07, 2.4362e-15, 3.6929e+00])
Graph break in user code at /tmp/ipykernel_699/215272159.py:4
Graph Break Reason: Attempted to call function marked as skipped
Explanation: Dynamo developers have intentionally marked that the function `save` in file `/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/torch/serialization.py` should not be traced.
Hint: Avoid calling the function `save`.
Hint: Apply `@torch._dynamo.dont_skip_tracing` to the function `save` to force tracing into the function. More graph breaks may occur as a result of attempting to trace into the function.
Hint: Please file an issue to PyTorch.
Developer debug context: module: torch.serialization, qualname: save, skip reason: <missing reason>
For more details about this graph break, please visit: https://meta-pytorch.github.io/compile-graph-break-site/gb/gb0007.html
User code traceback:
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/runpy.py", line 196, in _run_module_as_main
return _run_code(code, main_globals, None,
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/runpy.py", line 86, in _run_code
exec(code, run_globals)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py", line 18, in <module>
app.launch_new_instance()
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/traitlets/config/application.py", line 1075, in launch_instance
app.start()
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ipykernel/kernelapp.py", line 739, in start
self.io_loop.start()
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/tornado/platform/asyncio.py", line 211, in start
self.asyncio_loop.run_forever()
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/asyncio/base_events.py", line 603, in run_forever
self._run_once()
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/asyncio/base_events.py", line 1909, in _run_once
handle._run()
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/asyncio/events.py", line 80, in _run
self._context.run(self._callback, *self._args)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ipykernel/kernelbase.py", line 519, in dispatch_queue
await self.process_one()
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ipykernel/kernelbase.py", line 508, in process_one
await dispatch(*args)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ipykernel/kernelbase.py", line 400, in dispatch_shell
await result
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py", line 368, in execute_request
await super().execute_request(stream, ident, parent)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ipykernel/kernelbase.py", line 767, in execute_request
reply_content = await reply_content
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ipykernel/ipkernel.py", line 455, in do_execute
res = shell.run_cell(
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/ipykernel/zmqshell.py", line 577, in run_cell
return super().run_cell(*args, **kwargs)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py", line 3006, in run_cell
result = self._run_cell(
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py", line 3061, in _run_cell
result = runner(coro)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/async_helpers.py", line 129, in _pseudo_sync_runner
coro.send(None)
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py", line 3266, in run_cell_async
has_raised = await self.run_ast_nodes(code_ast.body, cell_name,
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py", line 3445, in run_ast_nodes
if await self.run_code(code, result, async_=asy):
File "/opt/conda/envs/py_3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py", line 3505, in run_code
exec(code_obj, self.user_global_ns, self.user_ns)
File "/tmp/ipykernel_699/215272159.py", line 9, in <module>
print(f(x))
File "/tmp/ipykernel_699/215272159.py", line 4, in f
torch.save(y, "foo.pt") # torch.save is an unsupported operation
torch.compile(f)(x) 的语义大致如下:
def compiled_f_semantics(x):
y = torch.compile(g, fullgraph=True)(x)
torch.save(y, "foo.pt")
z = torch.compile(h, fullgraph=True)(x)
return z
def g(x):
return x ** 2 / 2
def h(x):
return y ** 3 / 6
守卫#
在跟踪代码时,torch.compile 会对运行时值做一些假设。在跟踪过程中,我们会生成“守卫”,这些守卫是用于检查这些假设的运行时检查。守卫会在后续调用已编译函数时运行,以确定我们是否可以重用先前编译的代码。运行时检查的示例包括常量值、类型和对象 ID。
下面是一个生成的守卫示例。TENSOR_MATCH 守卫会检查输入的类型、设备、dtype、形状等。
@torch.compile
def fn(x):
return x + 1
print(fn(torch.ones(3, 3)))
tensor([[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.]])
GUARDS:
TREE_GUARD_MANAGER:
+- RootGuardManager
| +- LAMBDA_GUARD: torch._functorch.aot_autograd.utils.top_saved_tensors_hooks ids == None # _dynamo/output_graph.py:688 in init_ambient_guards
| +- DEFAULT_DEVICE: utils_device.CURRENT_DEVICE == None # _dynamo/output_graph.py:676 in init_ambient_guards
| +- GLOBAL_STATE: ___check_global_state()
| +- TORCH_FUNCTION_MODE_STACK: ___check_torch_function_mode_stack()
| +- GuardManager: source=L['x'], accessed_by=FrameLocalsGuardAccessor(key='x', framelocals_idx=0), type=<class 'torch.Tensor'>, tag_safe=(True, False)
| | +- TENSOR_MATCH: check_tensor(L['x'], Tensor, DispatchKeySet(CPU, BackendSelect, ADInplaceOrView, AutogradCPU), torch.float32, device=None, requires_grad=False, size=[3, 3], stride=[3, 1]) # return x + 1 # mp/ipykernel_699/1068332425.py:3 in fn
| | +- NO_HASATTR: hasattr(L['x'], '_dynamo_dynamic_indices') == False # return x + 1 # mp/ipykernel_699/1068332425.py:3 in fn
Guard eval latency = 569.96 us
重新编译#
如果先前编译代码的每个实例的守卫都失败,那么 torch.compile 必须“重新编译”该函数,这需要再次跟踪原始代码。在下面的示例中,由于检查张量参数形状的守卫失败,因此需要重新编译。
@torch.compile
def fn(x):
return x + 1
print(fn(torch.ones(3, 3)))
print(fn(torch.ones(4, 4)))
tensor([[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.]])
tensor([[2., 2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2., 2.]])
Recompiling function fn in /tmp/ipykernel_699/420870727.py:1
triggered by the following guard failure(s):
- 3/0: tensor 'x' size mismatch at index 0. expected 3, actual 4
动态形状#
torch.compile 最初假设张量形状是静态/恒定的,并基于这些假设进行守卫。通过使用“动态形状”,我们可以让 torch.compile 生成可以接受不同形状的张量输入的已编译代码 - 我们避免了每次形状不同时都重新编译。默认情况下,在 torch.compile(dynamic=None) 中启用了自动动态形状 - 如果由于形状不匹配导致编译失败,则会尝试使用动态形状进行重新编译。动态形状也可以完全启用(dynamic=True)或禁用(dynamic=False)。
下面,我们启用了动态形状,并注意到我们不再需要重新编译。
@torch.compile(dynamic=True)
def fn(x):
return x + 1
print(fn(torch.ones(3, 3)))
print(fn(torch.ones(4, 4)))
tensor([[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.]])
tensor([[2., 2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2., 2.]])
create_env
create_symbol s77 = 3 for L['x'].size()[0] [2, int_oo] return x + 1 # mp/ipykernel_699/1458103805.py:3 in fn (_dynamo/variables/builder.py:3508 in <lambda>), for more info run with TORCHDYNAMO_EXTENDED_DEBUG_CREATE_SYMBOL="s77" or to suppress this message run with TORCHDYNAMO_EXTENDED_ADVICE="0"
create_symbol s77 duck sized L['x'].size()[1]
eval False == False [statically known]
eval False == False [statically known]
produce_guards
track_symint L['x'].size()[0] s77 None
track_symint L['x'].size()[1] s77 None
track_symint L['x'].stride()[0] s77 None
track_symint L['x'].stride()[1] 1 None
track_symint L['x'].storage_offset() 0 None
Skipping guard L['x'].stride()[1] == 1
Skipping guard L['x'].storage_offset() == 0
有关动态形状的更多信息,请参阅 动态形状手册。
