Rendezvous#
创建于: 2021年5月4日 | 最后更新于: 2024年5月22日
在 Torch Distributed Elastic 的上下文中,我们使用“rendezvous”(会合/碰头)一词来指代一种结合了分布式同步原语和对等发现的特定功能。
Torch Distributed Elastic 使用它来收集训练作业的参与者(即节点),以便它们都就参与者列表及其各自的角色达成一致,并就何时可以开始/恢复训练做出一致的集体决策。
Torch Distributed Elastic rendezvous 提供了以下关键功能:
Barrier(屏障):
执行 rendezvous 的节点将全部阻塞,直到 rendezvous 被认为完成为止——当至少有 min 个总节点加入 rendezvous 屏障(对于同一作业)时,即完成。这也意味着屏障的大小不一定是固定的。
在达到 min 个节点后,还会有一个小的额外等待时间——这用于确保 rendezvous 不会“过快”完成(这可能会排除在同一时间尝试加入的额外节点)。
如果屏障收集到 max 个节点,rendezvous 将立即完成。
还有一个总体超时机制,如果从未达到 min 个节点,rendezvous 将失败——这旨在作为一种简单的故障安全措施,以帮助释放部分分配的作业资源,以防资源管理器出现问题,并且不应被视为可重试的。
Exclusivity(排他性):
简单的分布式屏障是不够的,因为我们还需要确保在任何给定时间(对于给定的作业)只存在一个节点组。换句话说,新节点(即迟到的节点)不应能够为同一个作业形成并行独立的 worker 组。
Torch Distributed Elastic rendezvous 确保如果一个节点组已经完成了 rendezvous(并因此可能已经在训练),那么试图进行 rendezvous 的其他“迟到”节点将仅宣布自己正在等待,并且必须等到(之前完成的)现有 rendezvous 首先被销毁。
Consistency(一致性):
当 rendezvous 完成时,所有成员都将就作业成员身份及其中的每个人的角色达成一致。这个角色用一个整数表示,称为 rank(秩),它介于 0 和 world_size 之间。
请注意,rank不稳定,因为同一个节点在下一次(重新)rendezvous 时可能会被分配不同的 rank。
Fault-tolerance(容错性):
Torch Distributed Elastic rendezvous 被设计为能够容忍 rendezvous 过程中的节点故障。如果在加入 rendezvous 和其完成之间发生进程崩溃(或失去网络连接等),则会自动使用剩余的健康节点进行重新 rendezvous。
节点还可能在完成 rendezvous(或被其他节点观察到已完成)之后发生故障——这种情况将由 Torch Distributed Elastic 的 train_loop 处理(它也将触发重新 rendezvous)。
Shared key-value store(共享键值存储):
当 rendezvous 完成时,会创建一个共享的键值存储并返回。此存储实现了 torch.distributed.Store API(参见 分布式通信文档)。
此存储仅由已完成 rendezvous 的成员共享。它旨在供 Torch Distributed Elastic 使用,以交换初始化作业控制和数据平面所需的信息。
Waiting workers and rendezvous closing(等待的 worker 和 rendezvous 关闭):
Torch Distributed Elastic rendezvous handler 对象提供了附加功能,这些功能在技术上不属于 rendezvous 过程。
查询有多少 worker 迟到屏障,它们可以参与下一个 rendezvous。
设置 rendezvous 为关闭状态,以通知所有节点不要参与下一个 rendezvous。
DynamicRendezvousHandler:
Torch Distributed Elastic 提供了 DynamicRendezvousHandler 类,该类实现了上述 rendezvous 机制。它是一种与后端无关的类型,在构造时需要指定一个 RendezvousBackend 实例。
Torch 分布式用户可以实现自己的后端类型,也可以使用 PyTorch 提供的以下实现之一:
C10dRendezvousBackend:使用 C10d 存储(默认为TCPStore)作为 rendezvous 后端。使用 C10d 存储的主要优点是它不需要第三方依赖项(如 etcd)即可建立 rendezvous。EtcdRendezvousBackend:取代了旧版的EtcdRendezvousHandler类。将EtcdRendezvousBackend实例传递给DynamicRendezvousHandler在功能上等同于实例化一个EtcdRendezvousHandler。store = TCPStore("localhost") backend = C10dRendezvousBackend(store, "my_run_id") rdzv_handler = DynamicRendezvousHandler.from_backend( run_id="my_run_id", store=store, backend=backend, min_nodes=2, max_nodes=4 )
下面是描述 rendezvous 如何工作的状态图。
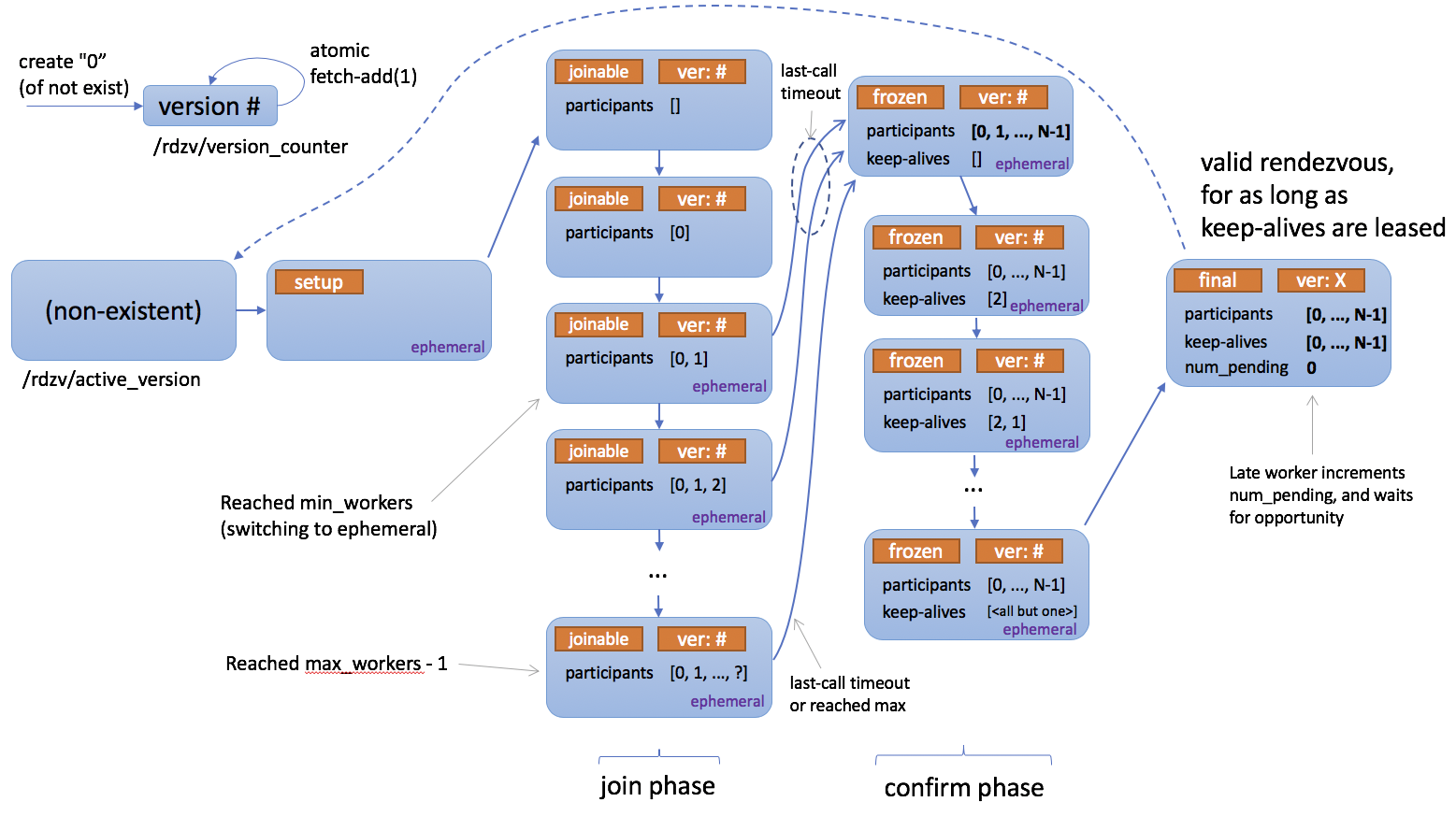
Registry(注册表)#
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.RendezvousParameters(backend, endpoint, run_id, min_nodes, max_nodes, local_addr=None, **kwargs)[source]#
保存用于构造
RendezvousHandler的参数。- 参数
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.RendezvousHandlerRegistry[source]#
代表
RendezvousHandler后端的注册表。
Handler(处理程序)#
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.RendezvousHandler[source]#
主要 rendezvous 接口。
注意
分布式 PyTorch 用户通常不需要实现自己的
RendezvousHandler。已提供基于 C10d Store 的实现,并且推荐给大多数用户使用。- abstract get_run_id()[source]#
返回 rendezvous 的 run id。
run id 是一个用户定义的 ID,用于唯一标识分布式应用程序的一个实例。它通常映射到作业 ID,并用于允许节点加入正确的分布式应用程序。
- 返回类型
- abstract is_closed()[source]#
检查 rendezvous 是否已关闭。
关闭的 rendezvous 意味着同一作业中所有未来的重新 rendezvous 尝试都将失败。
is_closed()和set_closed()具有最终传播的语义,不应用于同步。其目的是,如果至少有一个节点决定作业已完成,它将关闭 rendezvous,其他节点也将很快观察到这一点并停止运行。- 返回类型
- abstract next_rendezvous()[source]#
rendezvous 屏障的主入口点。
阻塞直到 rendezvous 完成并且当前进程包含在形成的 worker 组中,或者发生超时,或者 rendezvous 被标记为已关闭。
- 返回
返回
RendezvousInfo实例。- 引发
RendezvousClosedError – rendezvous 已关闭。
RendezvousConnectionError – 与 rendezvous 后端的连接失败。
RendezvousStateError – rendezvous 状态损坏。
RendezvousTimeoutError – rendezvous 未按时完成。
- 返回类型
- abstract num_nodes_waiting()[source]#
返回迟到 rendezvous 屏障的节点数量,这些节点未包含在当前 worker 组中。
调用者应定期调用此方法以检查是否有新节点正在等待加入作业,如果有,则通过调用
next_rendezvous()(重新 rendezvous)来接纳它们。- 返回类型
- abstract shutdown()[source]#
关闭为 rendezvous 打开的所有资源。
示例
rdzv_handler = ... try: store, rank, world_size = rdzv_handler.next_rendezvous() finally: rdzv_handler.shutdown()
- 返回类型
- property use_agent_store: bool#
指示通过
next_rendezvous()返回的 store 引用可以与用户应用程序共享,并在应用程序生命周期内可用。Rendezvous handler impl 将 store 详细信息作为
RendezvousStoreInfo的实例共享。应用程序通常使用 MASTER_ADDR/MASTER_PORT 环境变量来查找 store。
Dataclasses(数据类)#
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.RendezvousInfo(store, rank, world_size, bootstrap_store_info)[source]#
保存 rendezvous 的信息。
Exceptions(异常)#
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.api.RendezvousTimeoutError[source]#
在 rendezvous 未按时完成时引发。
Implementations(实现)#
Dynamic Rendezvous(动态 Rendezvous)#
- torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.dynamic_rendezvous.create_handler(store, backend, params)[source]#
根据指定参数创建一个新的
DynamicRendezvousHandler。- 参数
store (Store) – 作为 rendezvous 的一部分返回的 C10d store。
backend (RendezvousBackend) – 用于保存 rendezvous 状态的后端。
- 返回类型
参数
描述
join_timeout
rendezvous 预计完成的总时间(秒)。默认为 600 秒。
last_call_timeout
在达到最小节点数后,在完成 rendezvous 之前的额外等待时间(秒)。默认为 30 秒。
close_timeout
在调用
RendezvousHandler.set_closed()或RendezvousHandler.shutdown()后,rendezvous 预计关闭的时间(秒)。默认为 30 秒。heartbeat
保持连接的心跳(heartbeat)预计完成的时间(秒)。
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.dynamic_rendezvous.DynamicRendezvousHandler[source]#
代表一个用于在一组节点之间设置 rendezvous 的处理程序。
- classmethod from_backend(run_id, store, backend, min_nodes, max_nodes, local_addr=None, timeout=None, keep_alive_interval=5, keep_alive_max_attempt=3)[source]#
创建一个新的
DynamicRendezvousHandler。- 参数
run_id (str) – rendezvous 的 run id。
store (Store) – 作为 rendezvous 的一部分返回的 C10d store。
backend (RendezvousBackend) – 用于保存 rendezvous 状态的后端。
min_nodes (int) – 允许进入 rendezvous 的最小节点数。
max_nodes (int) – 允许进入 rendezvous 的最大节点数。
timeout (Optional[RendezvousTimeout]) – rendezvous 的超时配置。
keep_alive_interval (int) – 节点在发送心跳以保持其在 rendezvous 中存活之前等待的时间。
keep_alive_max_attempt (int) – 在节点被视为死亡之前,失败的心跳尝试次数。
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.dynamic_rendezvous.RendezvousBackend[source]#
代表一个保存 rendezvous 状态的后端。
- abstract get_state()[source]#
获取 rendezvous 状态。
- 返回
编码的 rendezvous 状态及其 fencing token 的元组,如果没有在后端找到状态则为
None。- 引发
RendezvousConnectionError – 与后端的连接失败。
RendezvousStateError – rendezvous 状态损坏。
- 返回类型
- abstract set_state(state, token=None)[source]#
设置 rendezvous 状态。
新的 rendezvous 状态是条件性设置的。
如果指定的
token与后端中存储的 fencing token 匹配,则状态将被更新。新的状态将与它的 fencing token 一起返回给调用者。如果指定的
token与后端中存储的 fencing token 不匹配,则状态不会被更新;相反,现有状态将与它的 fencing token 一起返回给调用者。如果指定的
token为None,则仅当后端中不存在现有状态时,才会设置新状态。新状态或现有状态及其 fencing token 将返回给调用者。
- 参数
state (bytes) – 编码的 rendezvous 状态。
token (Optional[Any]) – 一个可选的 fencing token,该 token 是通过之前调用
get_state()或set_state()获取的。
- 返回
序列化的 rendezvous 状态、其 fencing token 以及一个指示设置尝试是否成功的布尔值的元组。
- 引发
RendezvousConnectionError – 与后端的连接失败。
RendezvousStateError – rendezvous 状态损坏。
- 返回类型
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.dynamic_rendezvous.RendezvousTimeout(join=None, last_call=None, close=None, heartbeat=None)[source]#
保存 rendezvous 的超时配置。
C10d Backend(C10d 后端)#
- torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.c10d_rendezvous_backend.create_backend(params)[source]#
根据指定参数创建一个新的
C10dRendezvousBackend。参数
描述
store_type
C10d store 的类型。当前支持的类型是“tcp”和“file”,分别对应
torch.distributed.TCPStore和torch.distributed.FileStore。默认为“tcp”。read_timeout
store 操作的读取超时时间(秒)。默认为 60 秒。
注意,这仅适用于
torch.distributed.TCPStore。它与torch.distributed.FileStore无关,后者不接受超时作为参数。is_host
一个布尔值,指示此后端实例是否将托管 C10d store。如果未指定,将通过将此机器的主机名或 IP 地址与指定的 rendezvous 端点进行匹配来推断。默认为
None。注意,此配置选项仅适用于
torch.distributed.TCPStore。在正常情况下,您可以安全地跳过它;唯一需要的时候是当其值无法正确确定时(例如,rendezvous 端点的主机名是 CNAME,或者不匹配机器的 FQDN)。
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.c10d_rendezvous_backend.C10dRendezvousBackend(store, run_id)[source]#
代表一个基于 C10d 的 rendezvous 后端。
- 参数
store (Store) – 用于与 C10d store 通信的
torch.distributed.Store实例。run_id (str) – rendezvous 的 run id。
Etcd Backend(Etcd 后端)#
- torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.etcd_rendezvous_backend.create_backend(params)[source]#
根据指定参数创建一个新的
EtcdRendezvousBackend。参数
描述
read_timeout
etcd 操作的读取超时时间(秒)。默认为 60 秒。
protocol
用于与 etcd 通信的协议。有效值为“http”和“https”。默认为“http”。
ssl_cert
用于 HTTPS 的 SSL 客户端证书路径。默认为
None。ssl_cert_key
用于 HTTPS 的 SSL 客户端证书私钥路径。默认为
None。ca_cert
根 SSL 证书颁发机构的路径。默认为
None。
Etcd Rendezvous (Legacy)(Etcd Rendezvous (遗留版))#
警告
DynamicRendezvousHandler 类取代了 EtcdRendezvousHandler 类,并且是大多数用户的推荐选择。EtcdRendezvousHandler 处于维护模式,未来将被弃用。
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.etcd_rendezvous.EtcdRendezvousHandler(rdzv_impl, local_addr)[source]#
实现了由
torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.etcd_rendezvous.EtcdRendezvous支持的torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.RendezvousHandler接口。EtcdRendezvousHandler使用 URL 来配置要使用的 rendezvous 类型,并将实现特定的配置传递给 rendezvous 模块。基本的 etcd rendezvous 配置 URL 如下所示:etcd://<etcd_address>:<port>/<job_id>?min_workers=<min_workers>&max_workers=<max_workers> # noqa: W605 -- example -- etcd://:2379/1234?min_workers=1&max_workers=3
上述 URL 的解释如下:
使用与
etcdscheme 注册的 rendezvous handler。要使用的
etcd端点是localhost:2379。job_id == 1234用作 etcd 中的前缀(这允许在共享公共 etcd 服务器的情况下,只要job_ids保证是唯一的,就可以支持多个作业)。请注意,作业 ID 可以是任何字符串(例如,不需要是数字),只要它是唯一的。min_workers=1和max_workers=3指定了成员资格大小的范围——只要集群大小大于或等于min_workers,Torch Distributed Elastic 就会开始运行作业,并允许最多max_workers个节点加入集群。
以下是可传递给 etcd rendezvous 的参数的完整列表:
参数
描述
min_workers
rendezvous 有效的最小 worker 数量。
max_workers
要接纳的最大 worker 数量。
timeout
next_rendezvous 预计成功执行的总超时时间(默认为 600 秒)。
last_call_timeout
在达到最小 worker 数量后的额外等待时间(“最后调用”(defaults to 30s))。
etcd_prefix
etcd 中的路径前缀(从 etcd 根目录开始),所有 etcd 节点都将在其中创建(默认为
/torchelastic/p2p)。
Etcd Store(Etcd 存储)#
当 etcd 用作 rendezvous 后端时,EtcdStore 是 next_rendezvous() 返回的 C10d Store 实例类型。
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.etcd_store.EtcdStore(etcd_client, etcd_store_prefix, timeout=None)[source]#
通过搭便车 rendezvous etcd 实例来实现 c10 Store 接口。
这是
EtcdRendezvous返回的 store 对象。
Etcd Server(Etcd 服务器)#
EtcdServer 是一个方便类,可以轻松地在子进程中启动和停止 etcd 服务器。这对于测试或单节点(多 worker)部署非常有用,因为手动设置一个 sidecar etcd 服务器比单独设置 etcd 服务器更方便。
警告
对于生产和多节点部署,请考虑正确部署高可用的 etcd 服务器,因为它是您分布式作业的单点故障。
- class torch.distributed.elastic.rendezvous.etcd_server.EtcdServer(data_dir=None)[source]#
注意
已在 etcd 服务器 v3.4.3 上进行测试。
在随机空闲端口上启动和停止本地独立 etcd 服务器。对于单节点、多 worker 启动或测试非常有用,其中 sidecar etcd 服务器比单独设置 etcd 服务器更方便。
此类会注册一个终止处理程序来在退出时关闭 etcd 子进程。此终止处理程序不是调用
stop()方法的替代品。以下回退机制用于查找 etcd 二进制文件:
使用环境变量 TORCHELASTIC_ETCD_BINARY_PATH。
如果存在,则使用
<this file root>/bin/etcd。使用
PATH中的etcd。
用法
server = EtcdServer("/usr/bin/etcd", 2379, "/tmp/default.etcd") server.start() client = server.get_client() # use client server.stop()
- 参数
etcd_binary_path – etcd 服务器二进制文件的路径(参见上方回退路径)。
